

Higher and foundation tiers
How would you go about measuring the mass of individual atoms? The problem is atoms are so small and their masses will be expressed in numbers that are not easy to visualise or relate to in any way, it would be difficult to relate the masses of atoms to any everyday object in any meaningful way. So rather having to deal with these very small and awkward numbers chemists use a relative scale when discussing the masses of atoms.
A relative scale is simply a measuring scale where the masses of atoms are compared with each other. Chemists picked the element carbon; and in particular one isotope of carbon; the carbon-12 isotope and assign it a mass of exactly 12 units. So on this scale 1 mass unit is 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon-12. There is nothing uniquely special or different about the element carbon to explain why it is used as the standard against which the masses of other elements are compared; indeed in the past chemists have used hydrogen and oxygen atoms as the standard against which the masses of other elements are compared.
However 1961 the isotope of carbon; 12C; was picked as the standard from which the masses of all other atoms would be compared. On the carbon-12 scale the 12C isotope is given an atomic mass of exactly 12 units.
The lightest element in the periodic table is hydrogen; an atom of hydrogen has a mass of 1.66 x 10-27kg. This is a very very small mass. However if we compare the mass of a hydrogen atom to an atom of carbon-12 it is 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon-12. That is it takes twelve atoms of hydrogen to equal the mass of one atom of carbon-12. Since carbon-12 has a mass of exactly 12 units then the hydrogen atoms must have a mass of 1 unit on this relative scale (relative just means compared to).
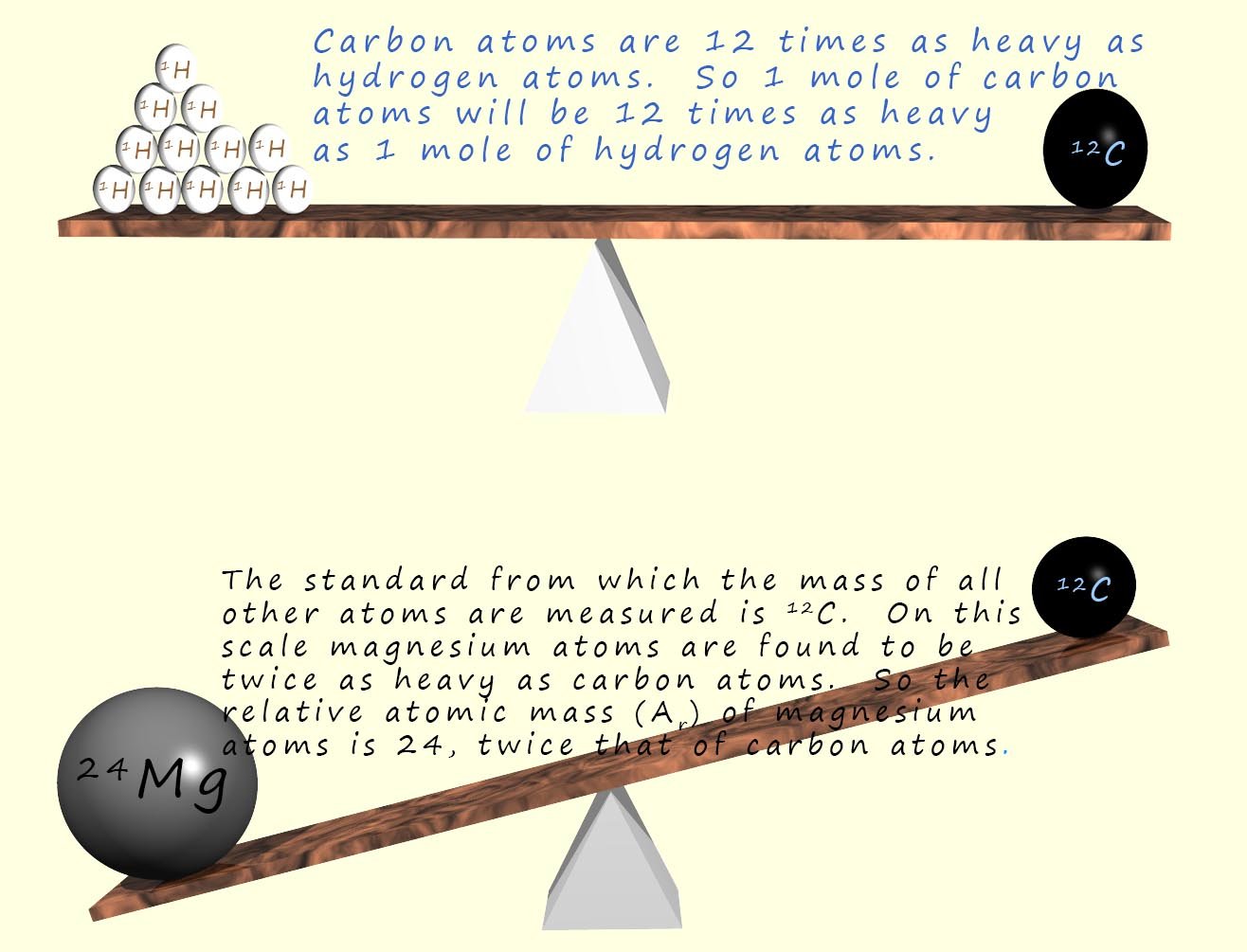
On this scale the mass of magnesium is 24, so magnesium atoms must be twice as "heavy" as carbon atoms. So we would say the relative atomic mass of magnesium is 24. This means that magnesium atoms have twice the mass of carbon atoms. The relative atomic mass of magnesium is therefore 24.
We use the symbol Ar for relative atomic mass. The relative atomic mass of an element has no units; it's a relative scale; however if you were to measure out the relative atomic mass for all elements in grams it will contain the same number of atoms; for example 1g of hydrogen, 12g of carbon, 24g of magnesium and 16g of oxygen all contain the same number of particles. Obviously the number of particles present will be huge; in fact the number is unbelievably huge; it's 6 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 00 atoms or 6 x 1023. This number is called Avogadro's number. It is the number of particles present in 1 mole of a substance.
A shortened version of the periodic table is shown below. For each element's symbol in the periodic table there are also two number in the box e.g. for magnesium the numbers 24 and 12 are alongside its symbol; Mg. The number 12 is the atomic number; the proton number. The other number is the relative atomic mass, Ar. It is the average mass of magnesium atoms taking into account the presence of any isotopes of magnesium. The mass of 1 mole of magnesium is simply the Ar expressed in grams, so 1 mole of magnesium is 24g and as mentioned above 1 mole of any substance contains 6 x 1023 particles or Avogadro's number of particles.

Examples using other elements from the periodic table.
The mass of 1 mole of an element is just the Ar expressed in grams
 Carbon dioxide is a small molecule made up of three atoms; 1 atom of
carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen.
Carbon dioxide is a small molecule made up of three atoms; 1 atom of
carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen.
To calculate the relative formula mass; Mr of this molecule is a simple task; simply add up
the relative atomic masses, (Ar) of each of the atoms present. The calculated mass of the molecule is called the relative
formula mass; it is given the symbol Mr.
 To avoid confusion and mix-ups great care needs to be taken to ensure you are very clear about
the type of particle you are discussing e.g. oxygen gas is a diatomic gas, this means that
exists as a molecule; formula O2.
To avoid confusion and mix-ups great care needs to be taken to ensure you are very clear about
the type of particle you are discussing e.g. oxygen gas is a diatomic gas, this means that
exists as a molecule; formula O2.
If we had 10 molecules of oxygen gas we would have 20 atoms of oxygen, since each molecule contains
2 atoms of oxygen. If we had 6x1023 molecules; that is 1 mole of molecules then we would
have 2x6x1023 atoms of oxygen present; that is 2 moles of oxygen atoms.
The relative atomic mass of an oxygen atom is 16;
Ar =16. So the mass of 1 mole of oxygen molecules (O2) is 32g. The mass of 1 mole of oxygen
atoms is 16g. To avoid confusion you must be clear about the type of
particle, atom, molecule or ion you are discussing.
Calculating the relative formula mass (Mr) of substances is a common exam question and one you are likely to meet; however calculating Mr values for compounds is easy and simply needs a little practice to become an expert at it; so why not master this by working out the relative formula masses for the compounds shown in the examples opposite?