Foundation and higher tiers

Metals are found in the left hand-side of the periodic table. In GCSE chemistry you will be mainly studying the reactions of the metals in groups I and II of the periodic table; that is the alkali metals and the alkaline earth metals. The alkali metals; Li, Na, K, Rb and Cs
in group 1 of the periodic table all have one electron in their outer shell. Recall the octet rule which states that: elements will only react if they can achieve
full last electron shells; this means that the alkali metals
with one outer shell electron will either have to gain 7
electrons to fill their last shell or
simply lose one electron when they react.
As an example consider the alkali metal sodium; atomic number 11, now sodium has the electronic configuration of 2,8,1 so to completely fill its last shell
the sodium atom needs to gain 7 electrons or simply lose the one outer electron in its outer shell or energy level.
Obviously it will be easier and require less energy to simply lose 1 electron than
gain 7 electrons.
So when sodium reacts it will lose its outer shell electron to another atom and this will mean that sodium now has an electronic configuration of 2,8; the same as the noble gas neon.
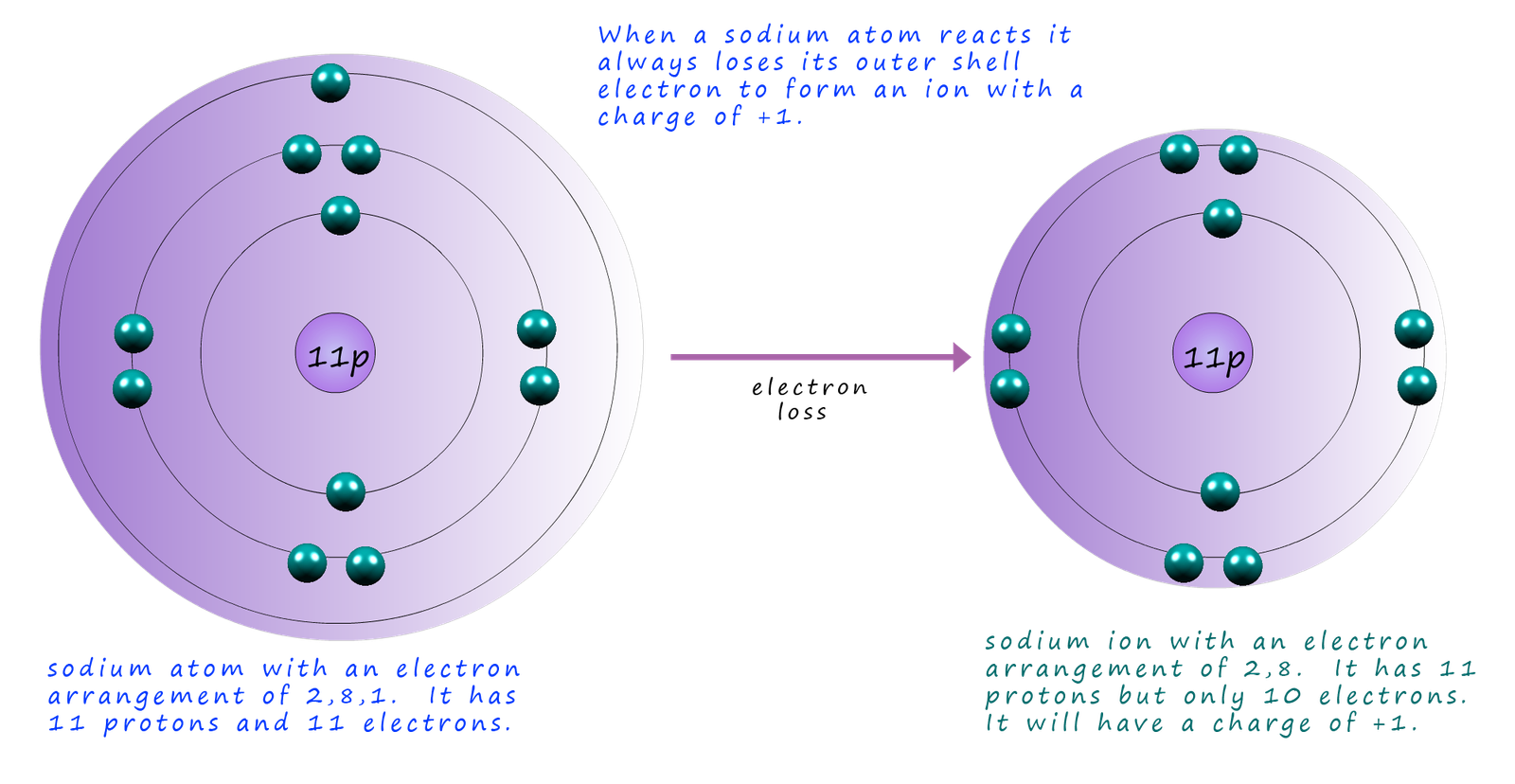
Metal atoms always lose electrons when they react with non-metals; this means they always end up with more positively charged protons than negatively charged electrons so metal ions are always positively charged. Again remembering that group I metals lose one electron and form ions with a 1+ charge while group II metals lose two electrons and so will end up forming ions with a 2+ charge. Similarly group III metals such as aluminium will lose 3 electrons and end up forming ions with a 3+ charge. This is summarised in the table below:
| Group in periodic table | number of electrons in the last shell | number of electrons lost | charge on ion | examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1+ | Li+, Na+, K+ |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 2+ | Mg2+, Ca+ |
| 3 | 3 | 3 | 3+ | Al3+ |
A similar thing happens with the reactive non-metals; these non-metals are mainly in groups 5, 6 and 7 of the periodic table. Non-metal elements in group 5 obviously have 5 electrons in their outer electron shell so they need to gain 3 electrons to achieve a full outer electron shell. However if they gain 3 electrons or 3 negative charges then they will have 3 more negatively charged electrons than positively charged protons in their nucleus; so they will end up with forming an ion with a 3- charge. A similar thing happens with the non-metals in groups 6 and 7, this is outlined in the table below which shows the charge on common non-metal ions.
| Group in periodic table | number of electrons in the last shell | number of electrons gained | charge on ion | examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 | 3 | 3- | N3-, P3- |
| 6 | 6 | 2 | 2- | O2-, S2- |
| 7 | 7 | 1 | 1- | F-, Cl-, Br- |
Answer the questions below to check your understanding on the main ideas covered above. Simply click the boxes to reveal the answers.
 Atoms do not have a charge, they are neutral. Atoms contain equal numbers of positively charged protons in their nucleus and negatively charged electrons in their electron shells.
Atoms do not have a charge, they are neutral. Atoms contain equal numbers of positively charged protons in their nucleus and negatively charged electrons in their electron shells. The metals such as Na, Li, Ca and Mg in groups I and II of the periodic table only contain 1 or 2 electrons in their outer electron shells and so when they react they will lose these electrons to the non-metal atom they are reacting with. This means that the metal atoms will now have more positively charged protons in the nucleus than negatively charged electrons in the electron shells. The metal atoms are now positively charged metal ions. These positively charged ions are often called cations.
The metals such as Na, Li, Ca and Mg in groups I and II of the periodic table only contain 1 or 2 electrons in their outer electron shells and so when they react they will lose these electrons to the non-metal atom they are reacting with. This means that the metal atoms will now have more positively charged protons in the nucleus than negatively charged electrons in the electron shells. The metal atoms are now positively charged metal ions. These positively charged ions are often called cations.
 An ionic bond is formed by the electrostatic attraction between negatively charged non-metal ions and a positively charged metal ions.
An ionic bond is formed by the electrostatic attraction between negatively charged non-metal ions and a positively charged metal ions.
Since metal atoms lose electrons when they react to achieve full outer electron shells and non-metal atoms gain electrons when
they react then it would seem obvious that metals and non-metals react readily together to form compounds made up of ions; that is
ionic compounds.
Ionic compounds consist of giant lattice made up of positively charged metal ions and negatively
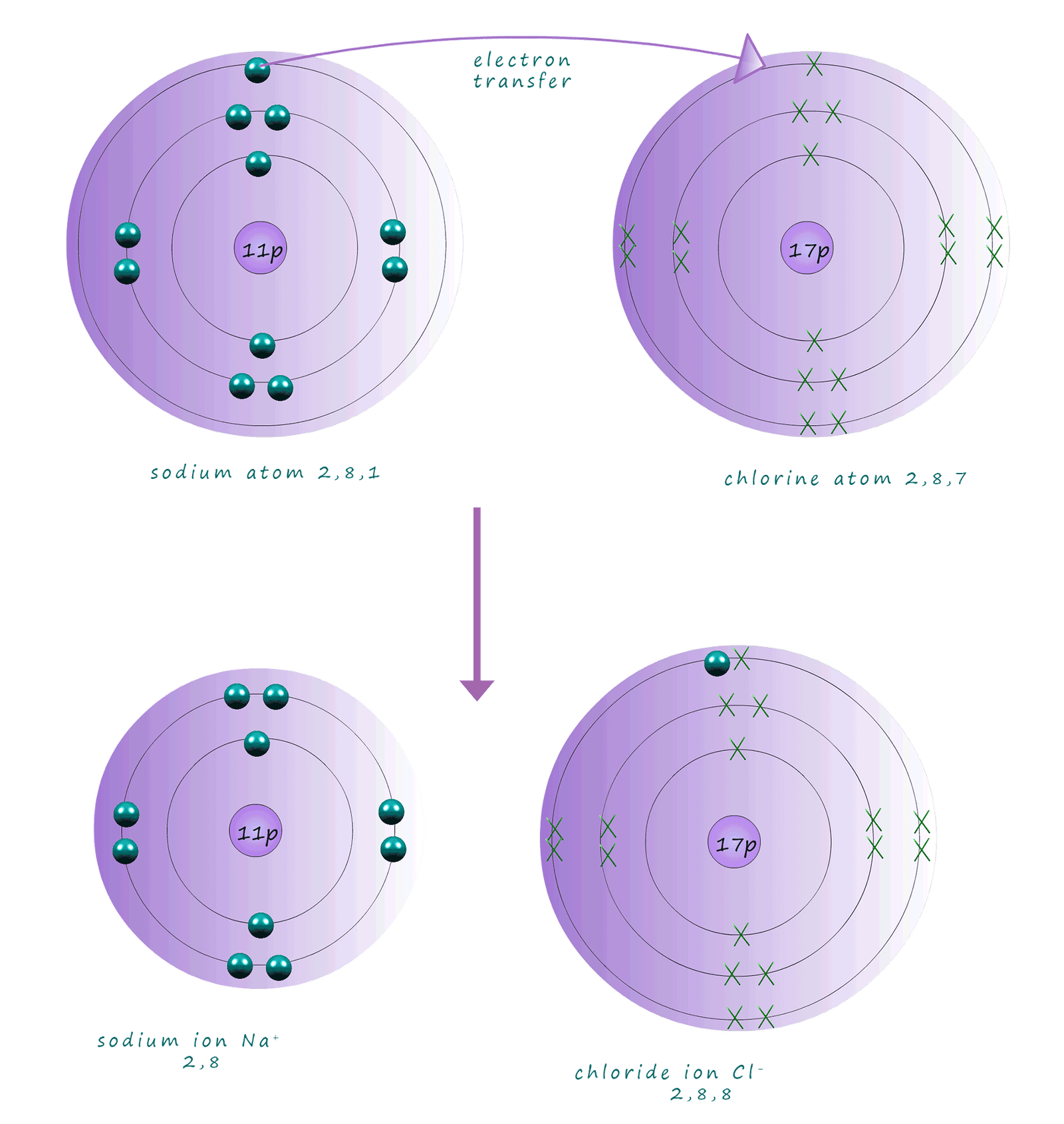
charged non-metal ions, for example consider the reaction between sodium metal; a group I alkali metal; electron arrangement 2,8,1 and the halogen chlorine from group 7 of the periodic table. Now chlorine has an atomic number of 17 and an electron arrangement of 2,8,7. To achieve full outer electron shells the sodium
atom needs to lose one electron and the chlorine atom needs to gain one electron.
So when sodium and chlorine react an electron is transferred from the sodium atom to the chlorine atom. We can
show what is happening in terms of electron transfer in the diagram below; here the electrons in the sodium atom are shown as solid balls whereas in the chlorine atom the electrons are shown as crosses, this is simply to help us keep track of the movement of electrons as the reaction taking place.
Normally when we draw dot and cross diagram only the electrons in the last shells or energy levels are drawn. The reason for this is simple; these are the only electrons that are involved forming the bonding between the atoms. So the dot and cross diagram above can be simplified; this time showing only the outer electrons:
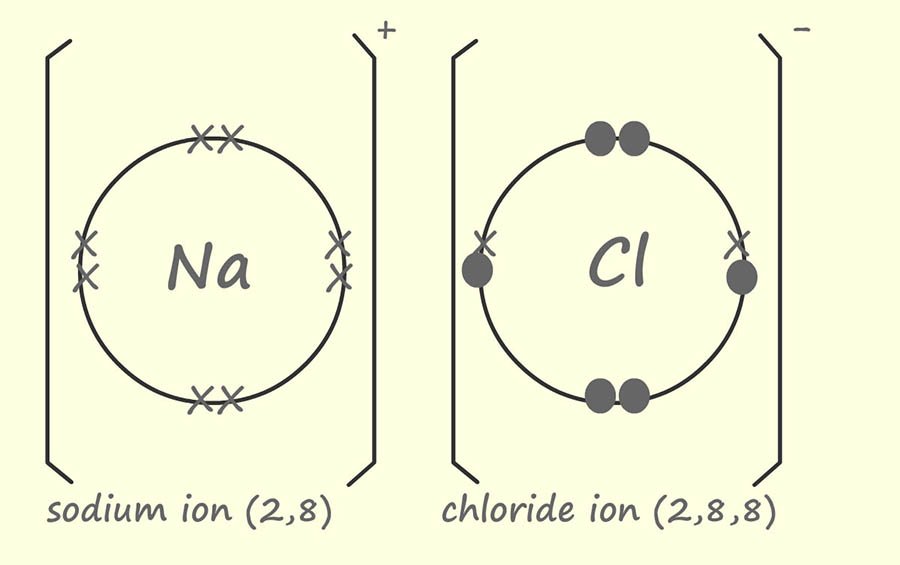
The positively charged sodium ion and the negative charged chloride ion produced are strongly attracted to each other since they have opposite charges. This type of attraction or bond is called an ionic bond. It is a type of electrostatic attraction.
Magnesium is an alkaline earth metal in group 2 of the periodic table, its electron arrangement is 2,8,2. This means that a magnesium atom will need to lose 2 electrons when it reacts to achieve a full outer electron shell. Chlorine as above is a halogen in group 7; its electron arrangement is 2,8,7 therefore chlorine only needs to gain one electron. Looks like we may have a bit of a problem! Magnesium atoms need to lose 2 electrons but chlorine atoms only need to gain 1 electron. The solution is simple; each magnesium reacts with 2 chlorine atoms with each chlorine atom accepting one electron from the magnesium. This is shown in the diagram below:
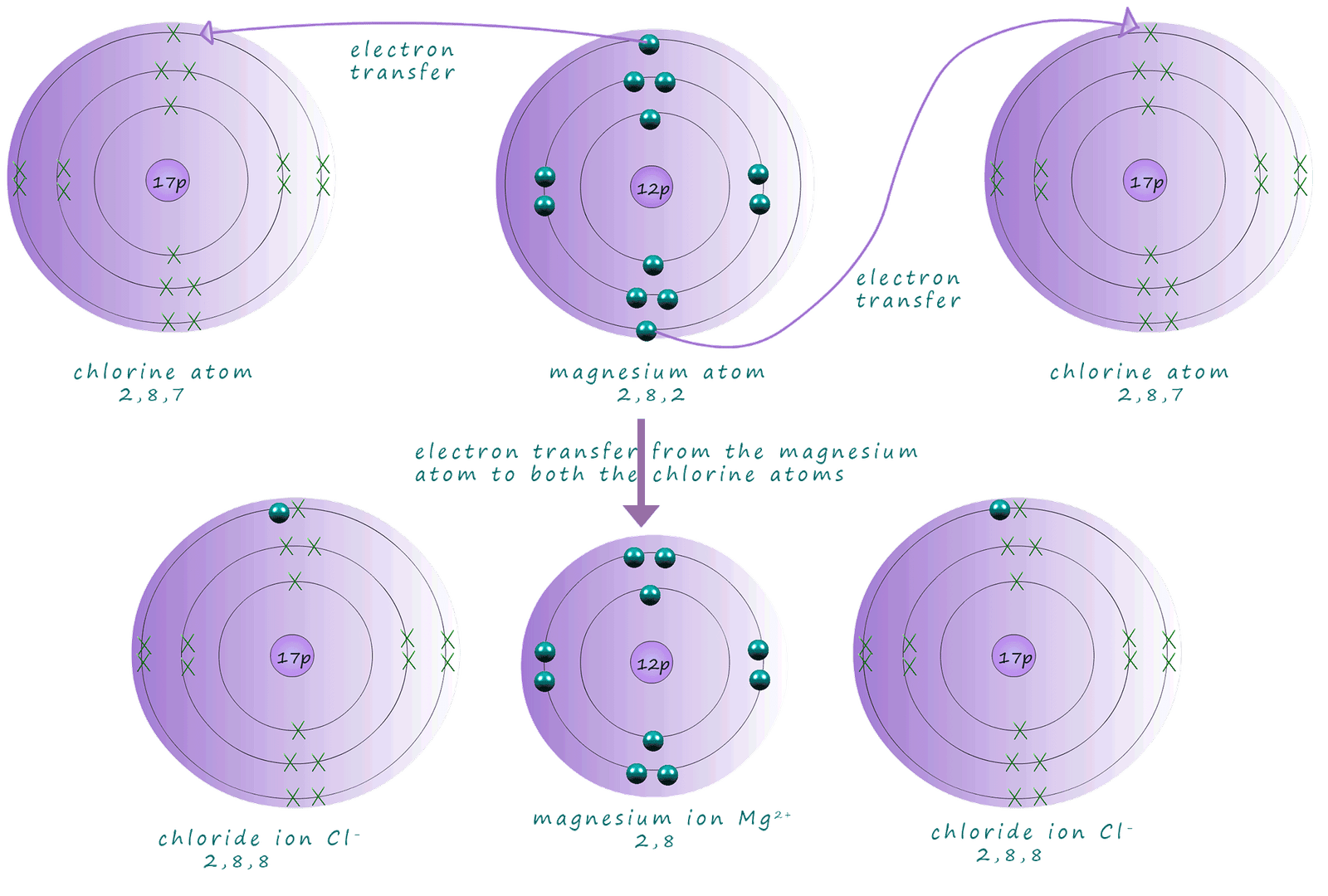
As before we can simplify the dot and cross diagram so that only the electrons that actually take part in the reaction/bonding, that is the outer shell electrons are shown:
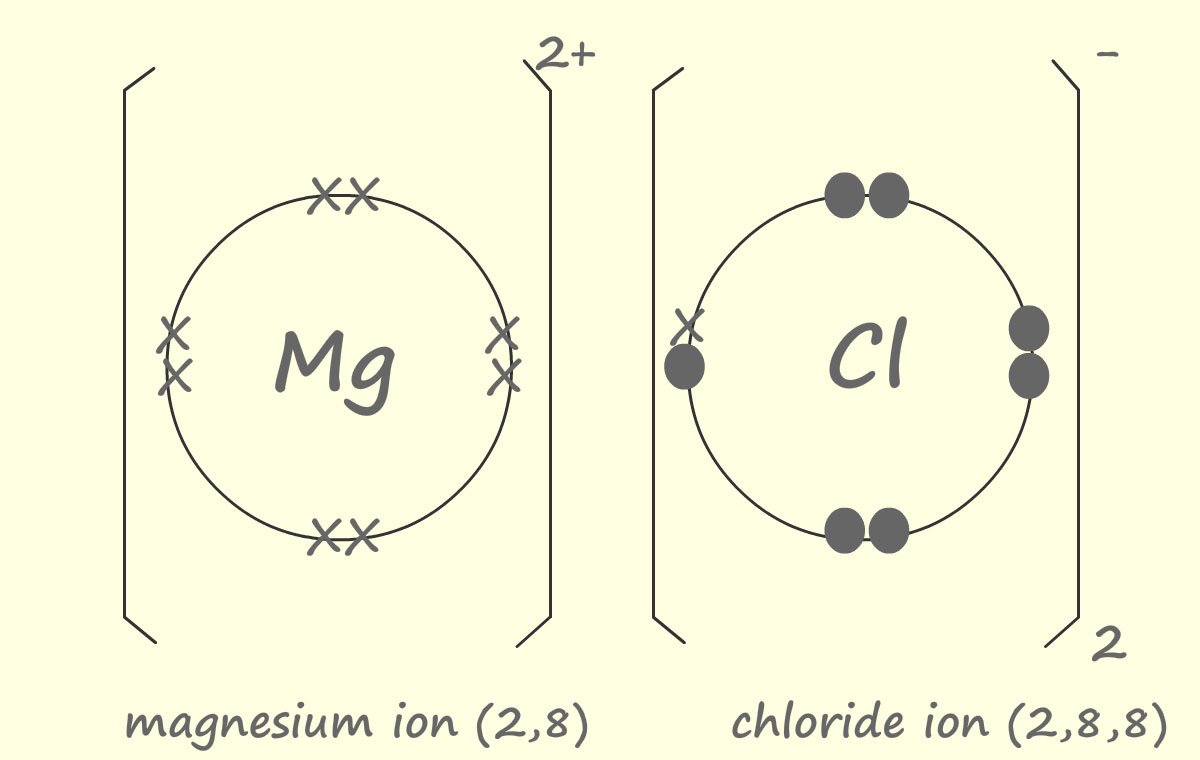
You may notice that when the atoms react they always end up with the same electron arrangement as a Noble gas- that is full outer electron shells.

Most of the discussion above has been about ions and how they are formed; however once you are confident about
how ions are formed
then it should be obvious that once positively and negatively charged ions are formed during a chemical reaction they will obviously attract each other, the attraction of oppositely charged ions is often called electrostatic attraction.
Therefore an ionic bond is simply the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. The large the charges present on the ions and the smaller the ions the stronger will be this electrostatic attraction.
Ionic compounds consist of giant structure of ions called a
lattice. Click on the link below or here for more information on the structure of ionic compounds.
Use the flash cards below to review your understanding of ions and ionic bonding.