

Higher and foundation tiers
The noble gases are found in the last column of the periodic table; group 0 (also called group 18). The noble gases are helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon and radon. Chemically they
are very unexciting as they tend not to react with other elements; with the exception mainly of the halogen fluorine but even then severe
conditions are needed and the compounds formed are not very stable- some even decompose explosively!
So why don't the noble gases react? Well if you remember the "Octet rule" which states that elements will only react if they can achieve
full outer electron shells and since all the noble gases already have full outer electron shells they have no reason to react with other elements.
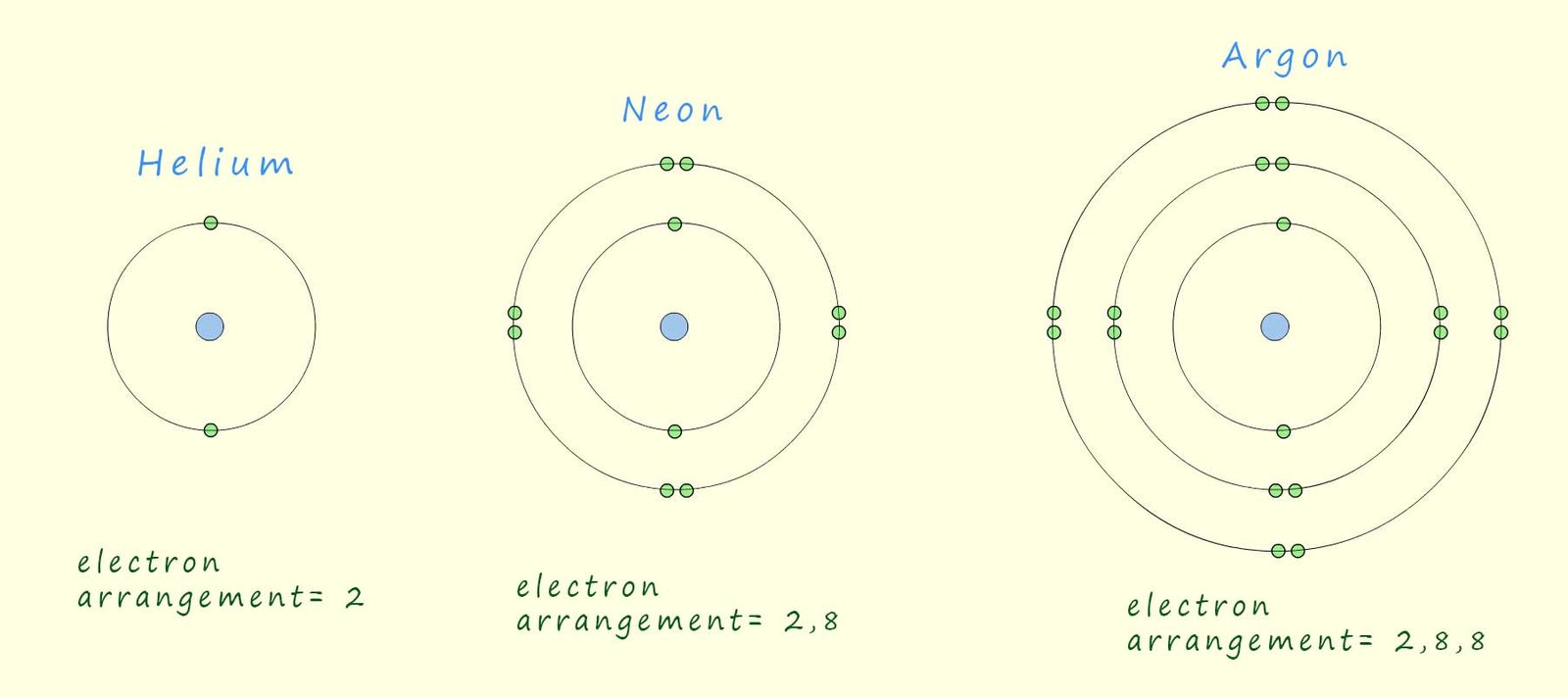
The three atomic structure diagrams below show the first three noble gases; helium, neon and argon and we can clearly see that all these elements have full outer electron shells or energy levels.
Many of the non-metal elements consist diatomic molecules, that is molecules which contain only two atoms e.g. oxygen gas (O2), nitrogen gas (N2), hydrogen gas, (H2) and all the halogens : fluorine gas (F2), Chlorine gas (Cl2), Bromine (Br2), iodine (I2) all have a molecular structure. However the noble gases are different; since they are reluctant to react they go around as single atoms and NOT molecules. They are often called monatomic gases (mono = one) since they consist of individual atoms.

 Since there is no real chemistry to study for the noble gases as they rarely react, we can however use the
periodic table to predict trends in their physical properties e.g. trends in the melting points (m.p.), boiling
points (b.p.) and their densities.
Since there is no real chemistry to study for the noble gases as they rarely react, we can however use the
periodic table to predict trends in their physical properties e.g. trends in the melting points (m.p.), boiling
points (b.p.) and their densities.
Since the noble gases consist of individual atoms their melting and boiling points will be very low. So what trend might we expect in the m.p. and b.p. as we go down group 0 from helium to radon? Well as we go down the group the atomic mass increases so we might expect the heavier atoms to have the highest melting and boiling points and this is exactly the trend we find. However this is not the whole story.
The atoms and molecules in all substances attract each other; these weak forces of attraction are called intermolecular bonds (think of an international as a competition between different countries) well intermolecular bonds are forces of attraction between adjacent atoms and molecules. They are caused by uneven electron distributions as the atoms and molecules approach each other. These intermolecular bonds are very weak when compared to normal covalent and ionic bonds but they can have a large effect on the physical properties of atoms and molecules.
The helium atoms in the diagram below as we know will not bond or join with each other as they already have full outer electron shells. However as the atoms in the helium gas get close to each other the atoms attract each other weakly - these are the intermolecular bonds.
However the strength of this intermolecular bonding increases as the atoms get larger in diameter and as the number of electrons in the atoms increase. Radon being the largest noble gas will have more and also stronger intermolecular bonds than helium. This is simply because it is a larger atom and has more surface area to form bonds with neighbouring atoms. The larger atomic mass and also increase in the amount and strength of the intermolecular bonding as we go down group 8 means that the melting and boiling points increase from helium to radon at the bottom of the group.
The diagrams below show the intermolecular bonding in the noble gases helium and radon gas. The dotted lines represent the intermolecular bonding between the individual atoms.
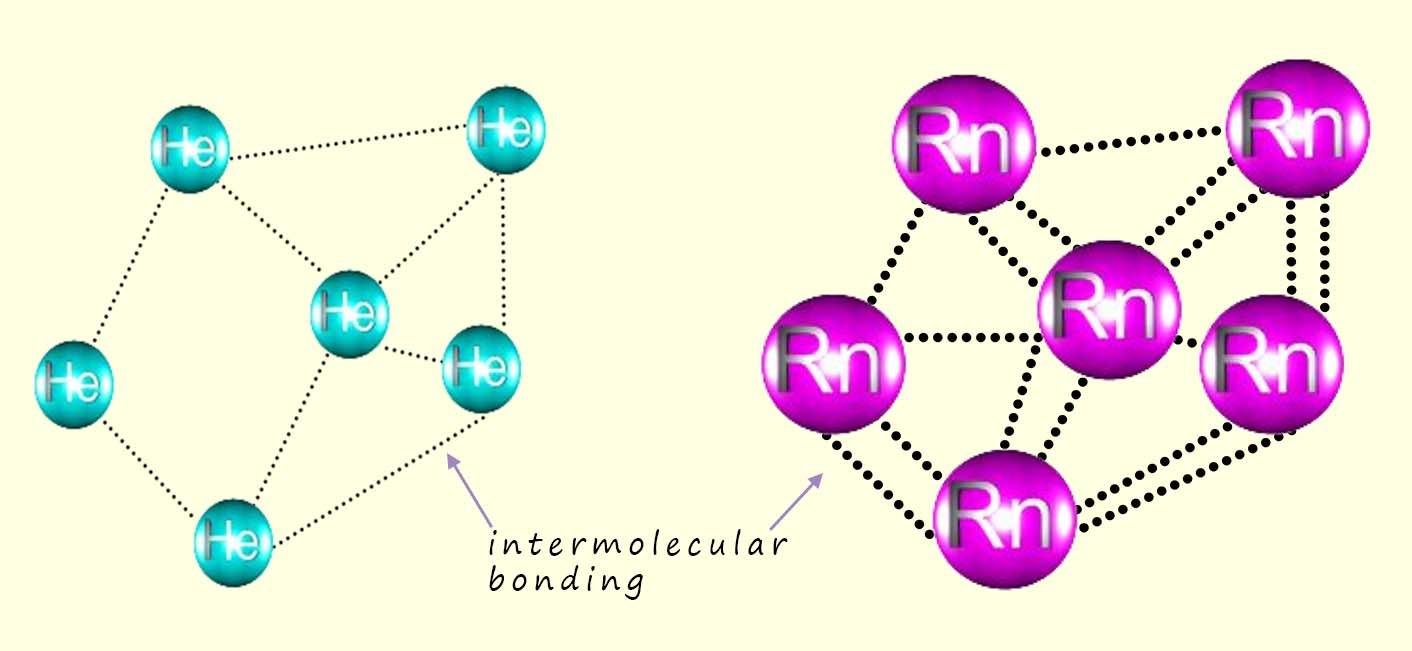
The amount of intermolecular bonding increases as the size of the atoms increases and the number of electrons in the atoms increase. Not only does the amount of intermolecular bonding increase as the atoms get larger; the strength of the intermolecular bonding also increases.
The table below clearly shows the trend in the melting points (m.p.) and boiling points (b.p.) of the group 0 noble gases. You will notice that the melting and boiling points are very low; this is completely expected as noble gases consist of individual atoms with weak intermolecular forces between these small individual atoms.
| Noble gas | Helium (He) | Neon (Ne) | Argon (Ar) | Krypton (Kr) | Xenon (Xe) | Radon (Rn) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| melting point/oC | -272 | -249 | -189 | -157 | -112 | -71 |
| boiling point/oC | -269 | -246 | -186 | -153 | -108 | -62 |
Density is how mass is inside a given volume. In the example below we have two gases; helium and radon inside two identical boxes. As you probably already know gases are mostly empty space. According to Avogadro's law equal volumes of gases will contain the same number of particles, in this case atoms. So the two identical boxes shown below obviously have the same volume and equal volumes of gases contain the same number of particles; so the boxes will contain the same number of atoms- obviously! Since radon atoms are heavier than helium atoms the box with the radon atoms weighs more than the box with the helium atoms and since density is how mass is inside a given volume the radon gas is more dense than the helium gas.
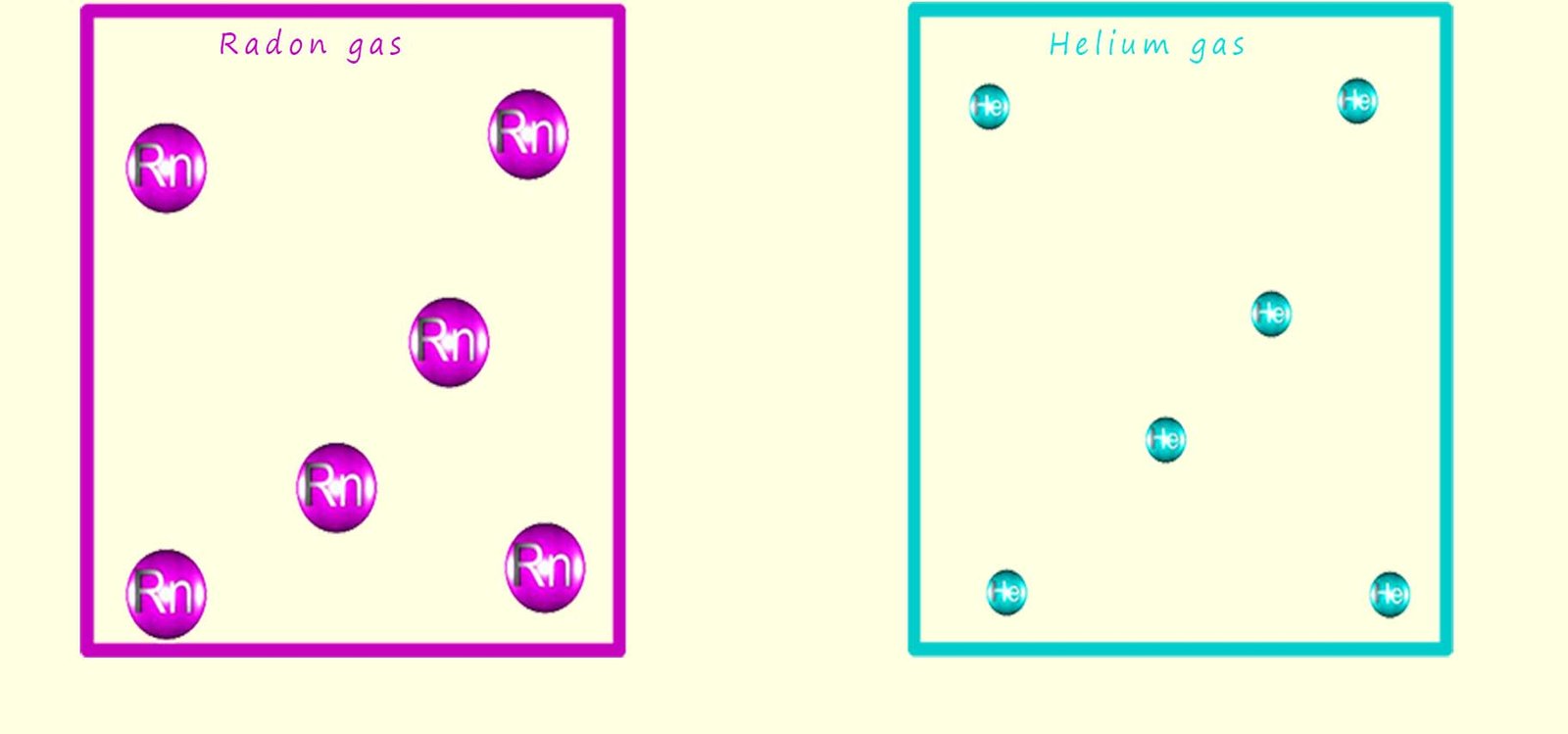
The formula for working out the density of a substance is density = mass/volume. Now the radon atoms have more mass than the helium atoms, and since both the boxes containing the two noble gases have the same volume; this means that radon gas has a larger density than the helium gas.
The density of the noble gases increases as you descend group 0. This can be easily demonstrated by simply filling balloons with different noble gases and allowing them to either rise or fall. Helium being the least dense noble gas rises very quickly in air while radon being the densest noble gas falls rapidly in air. This is shown in the image below:
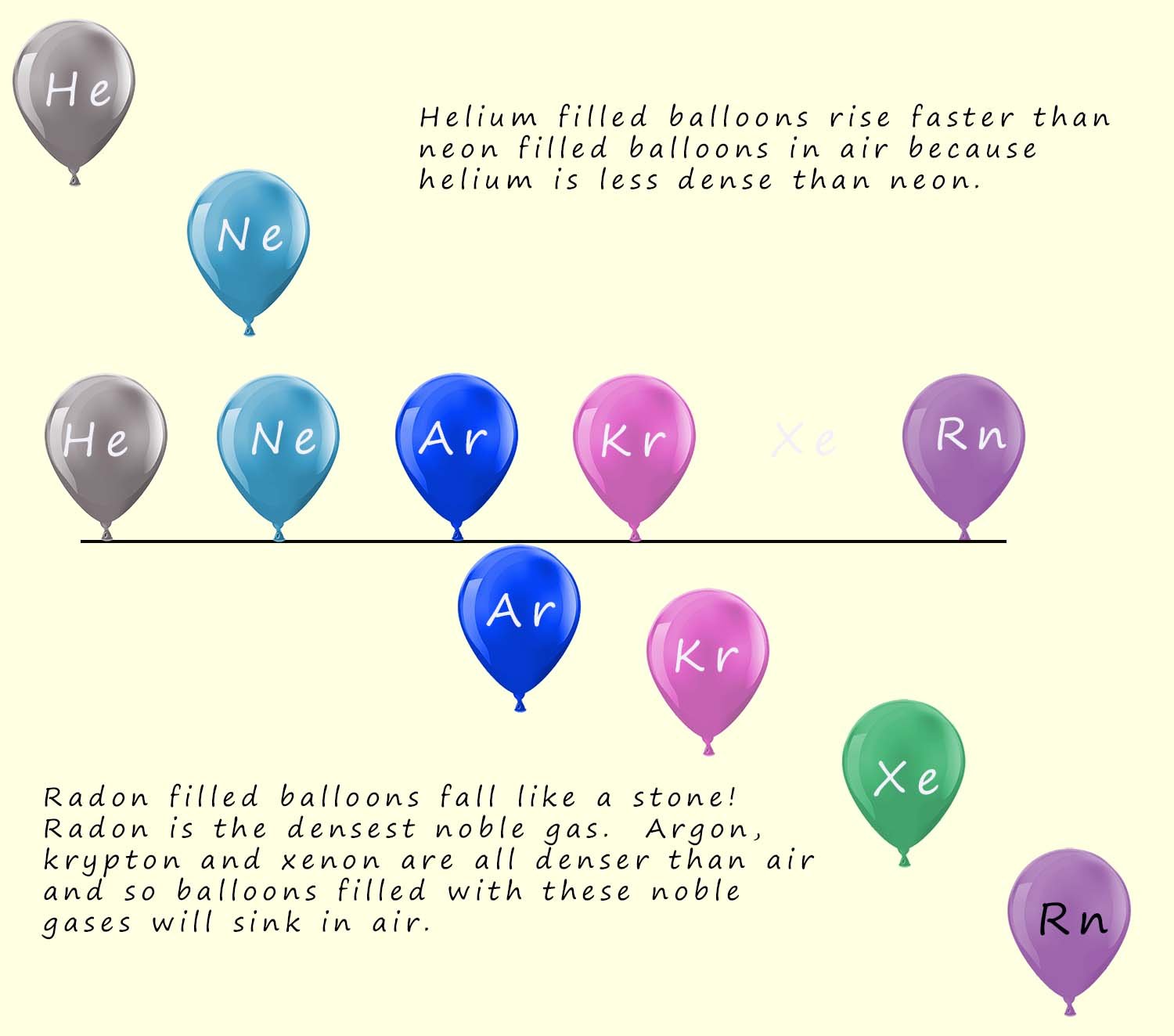
Use your knowledge of the densities of the noble gases to predict which of the noble gas filled balloons below rise and which will sink. Which balloon will rise most quickly in air and which balloon will sink fastest in the air?
Helium & Neon rise (less dense than air). Argon, Krypton, Xenon, Radon sink (denser than air).
 Having little or no chemistry the uses of the noble gases are limited. Most uses rely on the fact that the
noble
gases have almost no chemical reactivity e.g.
Light bulb filaments are made of the metal tungsten which glows white hot when the bulb is in
use. If the light bulb was simply filled with air then the filament would burn out almost as soon as
it was switched on. So filling the bulb with an inert noble gas like argon will prevent the filament
from burning out.
Having little or no chemistry the uses of the noble gases are limited. Most uses rely on the fact that the
noble
gases have almost no chemical reactivity e.g.
Light bulb filaments are made of the metal tungsten which glows white hot when the bulb is in
use. If the light bulb was simply filled with air then the filament would burn out almost as soon as
it was switched on. So filling the bulb with an inert noble gas like argon will prevent the filament
from burning out.

During welding a metal is heated well above its melting point and it can be easily
oxidised by reacting with oxygen in the air. This will weaken the metal and spoil the weld. So to
protect the hot metal during welding it is given a blanket of inert noble gas argon. Since argon is denser
than air and chemically unreactive it will keep out the oxygen and prevent the metal being oxidised.
Another use for argon gas is in argon lasers which are used in eye surgery and for creating holographs.
If neon gas is placed in a glass tube and a large enough voltage applied across it then the gas can be
made to emit light. These neon lights and signs are common on most high streets where they are used on
night clubs, restaurants, arcades and advertising signs.
Helium is mainly used in weather balloons and since its boiling point is so low, -2690C,
liquid helium is used to cool super-conducting magnets that hospital body scanners need to work
properly e.g. MRI scanners. The main use for krypton is to fill energy saving light bulbs and
in photography flashes.
Quickly review your understanding of the main uses of the noble gases by clicking on the noble gases and its uses.
Use the flashcards below to test your understanding of some of the main points on the properties and structure of the noble gases.



