Higher and foundation tiers
Concentration and rates of reaction
Concentration is the number of particles in a given volume. If you
increase the concentration then you increase
the number of particles present in any given volume; this means that there is more of a chance that the particles
will
collide successfully (see image below). If there are more successful collisions then the rate of reaction will increase.

The reaction of hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate
As a simple example of how concentration affects the rate of a reaction consider the reaction of hydrochloric acid with marble chips (calcium carbonate); equations for this reaction are shown below:
calcium carbonate(s) + hydrochloric acid(aq) → calcium chloride(aq) + carbon dioxide(g) + water(l)
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H20(l)
There are a number of ways in which you could measure the rate of this reaction; including:
-
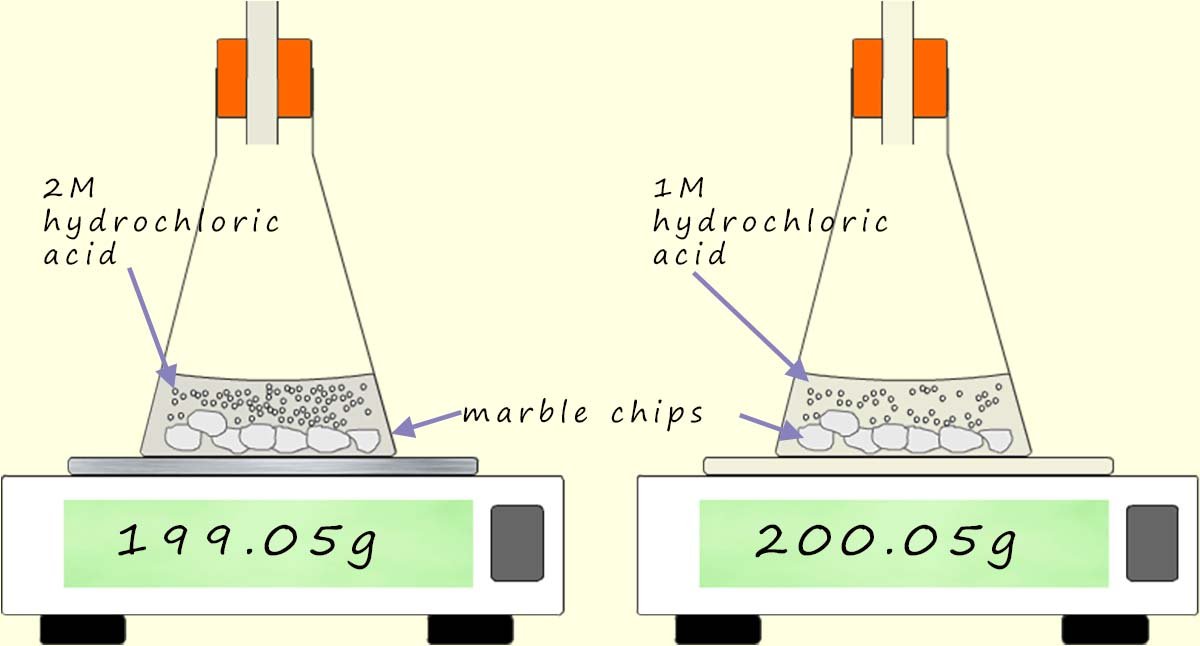
How quickly the bubbles of carbon dioxide are released in this reaction gives an excellent indication of how fast the reaction is going. If equal volumes of hydrochloric acid with different concentrations are added to two identical conical flasks containing the same sized pieces and an equal masses of marble chips then the rate or speed of the reaction can be quickly measured just by observing how quickly the bubbles of CO2 are released or by placing the two flasks onto a balance and recording the loss is mass as the heavy gas carbon dioxide is released. The faster the reaction the faster the carbon dioxide gas will be released and the more the mass reading on the balance will decrease; this is shown below:
- Alternatively instead of measuring a change in mass or counting bubbles you could simply use a gas syringe and measure how much carbon dioxide gas (CO2) is collected say every 10 or 15 seconds. This experiment would then be repeated using hydrochloric acid with different concentrations and then it would be easy to make a comparison of the volume of carbon dioxide gas released for each acid concentration, an apparatus set-up for this experiment is shown below:

Variables
 In each of the experiments outlined above the variables are:
In each of the experiments outlined above the variables are:
- The independent variable is simply the variable that you decide to change, so in this case it will be the concentration of the hydrochloric acid.
- The dependent variable is the variable you measure, so in this case it could be:
- The loss in mass as the carbon dioxide gas escapes from the conical flask. The loss in mass would simply be worked out from the reading on the balance.
- The other option would be to measure the volume of carbon dioxide gas released; again this is easily worked out from the reading on the gas syringe.
- The control variables are any other variable that could affect the results, these control variables are therefore variables other than the independent variable which could affect the results and so they must be controlled or kept constant. The control variables include:
- The volume of hydrochloric acid.
- The temperature of the hydrochloric acid.
- The surface area of the marble chips.
Concentration and gases
The particles in a gas are spread out with large areas of empty space between them meaning that there are large gaps between them.
This means that the chances of the particles in two different gases colliding and reacting with each other are quite low. To increase the chances
of these particles colliding with each other we can increase the pressure. Increasing the
pressure causes the particles to be squashed
closer together; this is the same as increasing the concentration of particles in a solutions. This is shown in the image below:

Key Points
- Increasing the concentration increases the number of particles in a given volume, more particles means more successful collisions and more
collisions means an increase in the reaction rate.
Practice questions
Next





 In each of the experiments outlined above the variables are:
In each of the experiments outlined above the variables are:
