

Chemistry only
Look around the room you are in and find an object made of metal. It could be for example a lamp, a chair leg, pen nib, stapler, a door handle, a musical instrument....... however the chances are that the metal object you have is not actually a pure metal but an alloy.
The way we use any particular material, including metals depends on their properties e.g.
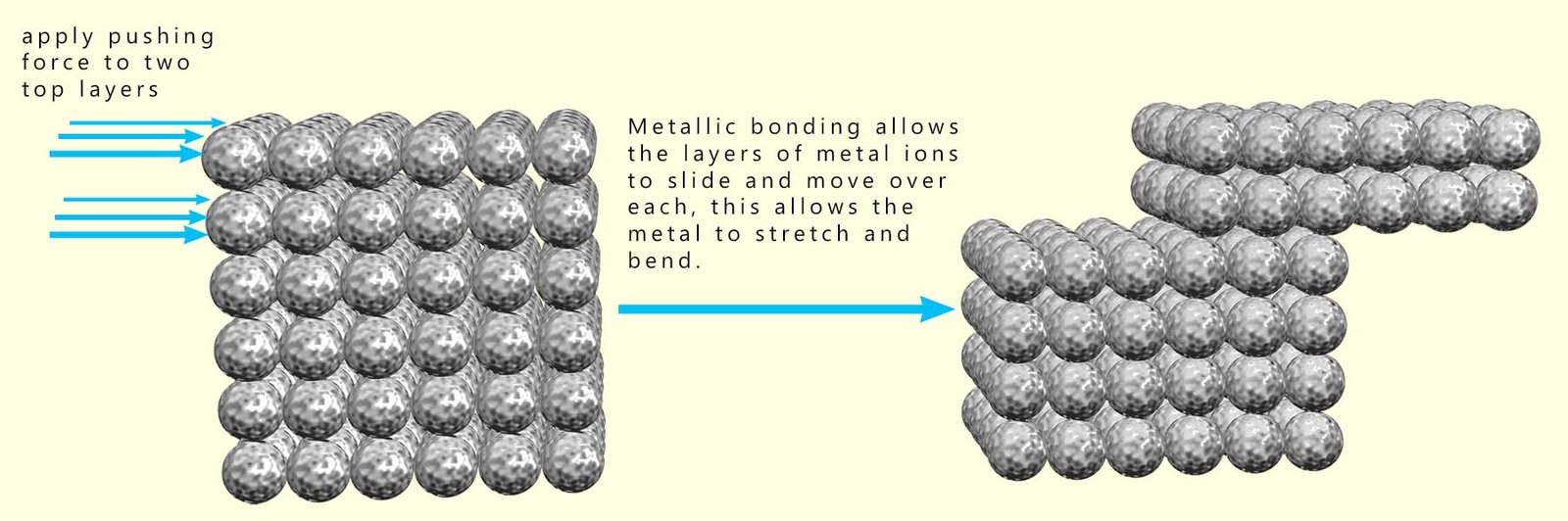
The physical properties of metals are generally fixed and are not easily changed, though for example it is possible to change the hardness and strength of some metals by simply hammering, bending and rolling them continually when they are cold. This cold hardening however only works on soft metals such as copper, aluminium, silver and gold. This cold hardening of metals works as follows:
However the changes to the properties of the metal that take place during this cold hardening are fairly small. So does this mean that the properties of metals are largely fixed and cannot be changed much? Well yes and no, it may not be possible to change the properties of most metals; but this is where alloys come in.


Consider pure gold which is often called 24 carat gold. Gold is a metal used in jewellery for its beauty and corrosion resistance. However pure gold is also a very soft metal and this undesirable property would limit its use in rings, necklaces and other items of jewellery. However when gold is mixed with other metals it forms gold alloys which are much harder than pure gold.
However adding these other metals can affect the colour of the
gold. Rose gold for example is a common alloy of gold; as its name
suggests it has a pinkish tint to it. This particular gold alloy is a mixture of 75% gold, 2.5% silver and 22.5% copper and it is much
harder than pure gold. Another alloy of gold which is commonly used in jewellery is
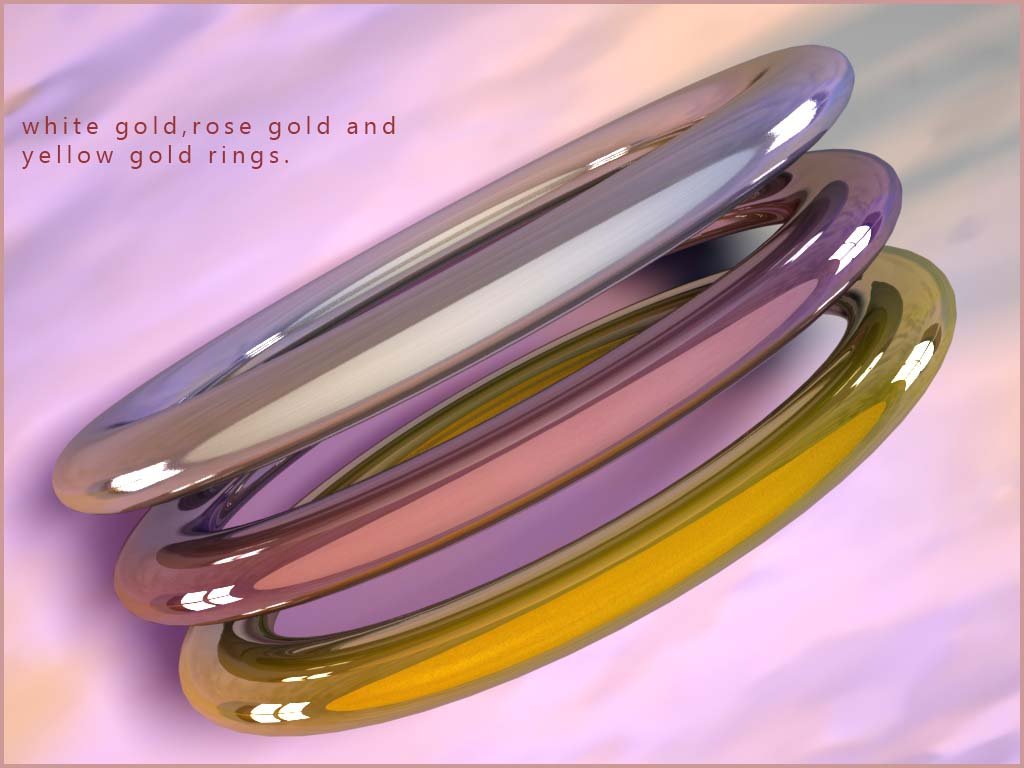
white gold. This is an alloy
containing gold which is mixed with the metals silver or even platinum or palladium and
as its name suggests white gold is not yellow
but has a silvery colour. The addition of platinum and/or palladium makes this alloy of gold hard and scratch
resistant but also very expensive.
Pure gold is referred to as 24 carat gold, while 18 carat
gold is 75% gold with other metals mixed through it; commonly copper and zinc are used.
18 carat gold is much harder than 24 carat gold
and is suitable for use in rings, necklaces and other items of jewellery.
12 carat gold is 50% gold and 9 carat gold
is 37.5% gold. 9 carat gold is commonly used in jewellery but is not as hard
as 18 carat gold or as resistant to corrosion and discolouration but it is less expensive since it contains less gold and more of the less expensive metals
copper and zinc.

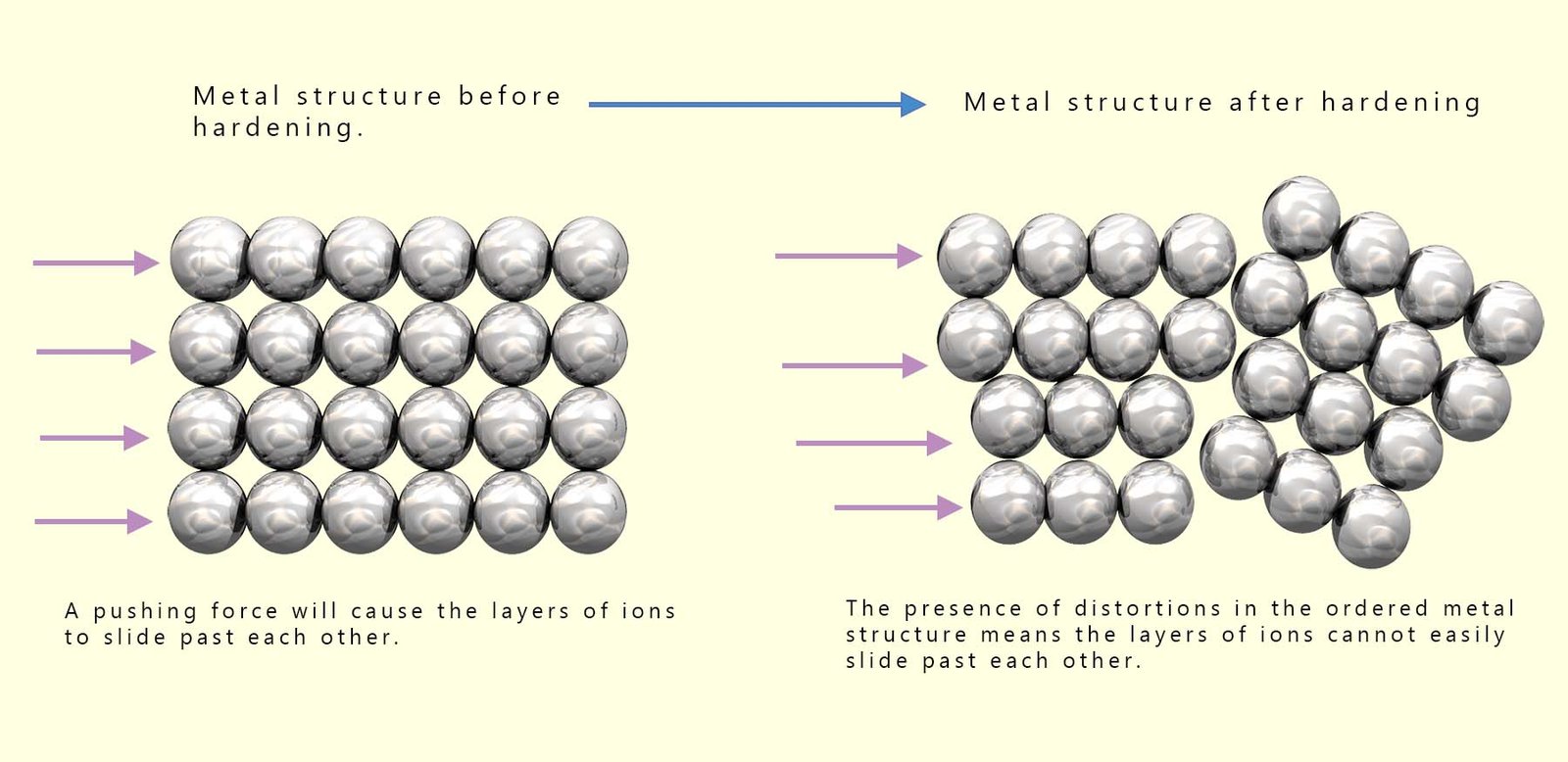
The diagram below illustrates why adding other elements, either metals or non-metals to an existing metal structure alters its properties. Metals are malleable which means that they can be hammered, beaten and rolled in different shapes. This occurs because the layers of ions in a giant metallic lattice structure are able to move and slide over each other if a large enough force is applied; this is outlined in the diagram below:
When other metals or non-metals are added and mixed in with the metal lattice the layers of metal ions present in the giant metallic lattice are not able to move or slide so freely over each other. This means that the alloy will be harder and stronger than the original metal. Depending on the size of the atoms which are mixed through the metal structure we can end up with alloys which have different types of structures.
Anything which stops these layers of metal ions from sliding when a force is applied will make the alloy stronger than the original metal. Alloys can be made simply by melting the main metal until it is a liquid then simply adding in the new metal or non-metal and stirring sufficiently until it dissolves. If the added metal/non-metal atoms are of a similar size to the existing metal ions they will substitute and replace the existing ions in the metal structure. This will form an alloy called a substitution alloy. Brass and bronze are examples of substitution alloys. If the added atoms are larger than the existing metal ions present, as shown below; then these new larger atoms will prevent the layers of metal ions from sliding and a much larger force will be needed to move the layers of metal ions. This will make the alloy much stronger with a larger tensile strength, it will also make it much harder.

If the added atom is much smaller than the existing metal ions in the metallic lattice then it will fit into the gaps between the metal ions, this is called an interstitial alloy; this is shown in the image above. These small atoms such as carbon and boron can bond to the metal ions in the metallic lattice and prevent them from moving as freely. This will result in a much stronger alloy but one which is much less ductile. Steel is an example of an interstitial alloy; it consists of iron with a small amount of the non-metal carbon. Steel can be turned into another alloy of steel called stainless steel by the addition of the transition metal chromium, this will result in a substitutional/interstitial alloy where the chromium atoms will substitute for iron atoms in the structure and the carbon will fit into the gaps between the iron ions. The addition of the metal chromium increases the strength and corrosion resistance of the alloy; this is outlined in the image above.
Using the information above decide whether each of the alloys in the activity below is a substitution, interstitial or substitution/interstitial alloy.
Decide whether each alloy is mainly a substitution alloy, an interstitial alloy, or a substitution / interstitial alloy.
| Alloy | Choose type | Feedback |
|---|
Everyone has probably heard a brass band or an orchestra with its brass section playing. Brass is a widely used alloy of copper and zinc, it is also an example of a substitution alloy. Brass has many common uses which take advantage of its properties of: durability, attractive gold like appearance, good thermal and electrical conductivity and excellent corrosion resistance.
Everyday objects which are made of brass include: locks, hinges, electrical plugs, gears, outdoor taps and fittings e.g. brass is widely used on boats fittings due to
its corrosion resistance properties. Brass is also commonly used in costume jewellery due to it attractive nature and
gold like appearance. Brass is also easy to cast into moulds making it ideal for making statues and models. Brass is also suitable
for use as fitting near flammable gases and liquids as it does not produce a spark when struck. Perhaps the best known use of brass is that is used to manufacture musical instruments such as trumpets, horns, trombones and tubas.
Copper is used for electrical wires because it is a good conductor of electricity, however brass is used to make the metal
pins in plugs because it is stronger, harder and very resistant to corrosion although it is not as good an electrical
conductor as copper
Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin; copper is the main metal used in this alloy with a percentage abundance of around 80-90% depending on the type of bronze used. Bronze is used mainly for statues and sculptures. Many Greek and Roman bronze sculptures still survive today due to their corrosion resistance.
The images below show some common alloys and their main uses:
Steel is an alloy of iron with other elements mixed in with it. There are many different types of steel and each type of steel has a different composition and as a result these different types of steel have different properties, this means that steels can be designed to suit it intended use.
Aluminium is a very useful metal because it is lightweight, malleable and naturally forms a thin layer of aluminium oxide on its surface which protects the metal from further corrosion. However, pure aluminium is quite soft, so it isn’t strong enough for many everyday uses. To alter and improve its properties, it is mixed with small amounts of other metals such as copper, magnesium, manganese and non-metals such as silicon to form aluminium alloys.
Aluminium alloys are much stronger and harder than pure aluminium but still keep their low density. This makes them ideal for building aircraft, where strength and low mass are essential. They are also used in cars, bicycles, ladders, drinks cans, and cooking foil. Different mixtures of aluminium alloys are chosen depending on the job — for example, stronger alloys for aircraft frames, and more flexible alloys for drinks cans.
One main advantage of aluminium alloys is that they keep aluminium’s natural resistance to corrosion, so they last a long time even when exposed to air and water. They are also light, strong, and easy to shape. Another benefit is that aluminium alloys can be recycled many times without losing their properties.
However, aluminium alloys do have some disadvantages. They are more expensive to produce than pure aluminium because of the extra metals used and the energy needed to make them. Some aluminium alloys are also harder to weld than other metals. Although they are strong, they are not as strong as steel, so they cannot be used in structures that need extremely high strength.
Overall, aluminium alloys offer an excellent balance of strength, low weight, and corrosion resistance, which is why they are used in so many modern applications.
Complete the activity below by choosing the correct alloy for each situation.
Read each situation and choose the best alloy for the job. You can change your mind – try to get them all correct!