

Chemistry only
Remember these key ideas about composite materials for your exam: 🧠
A composite material is a material made from two or more different materials that have very different physical or chemical properties. When these materials are combined, they form a new composite material with improved properties compared to the individual components. This allows scientists and engineers to design composite materials that are stronger, lighter, tougher, or more durable than the original materials alone. The aim in making these new materials is to take advantage of the best features of each component to create a new material that is perfectly suited to a particular job or product.
The idea behind composite materials is simple: combine two or more materials to make something better. By carefully selecting the right combination, manufacturers can produce a composite material that has only the useful or desirable properties of the starting materials while minimising their weaknesses or unwanted properties. For example, a composite material may be designed to be both strong and lightweight, or flexible and impact-resistant. This idea is not new — one of the earliest known composite materials was made thousands of years ago by the ancient Egyptians, who mixed mud with straw to build strong, durable bricks for their homes. The image below shows a simple model of how a composite material can be structured to achieve these enhanced properties.
The image below explains the basic idea behind composite materials and how scientists and engineers can change the properties of materials by combining them in a certain way.
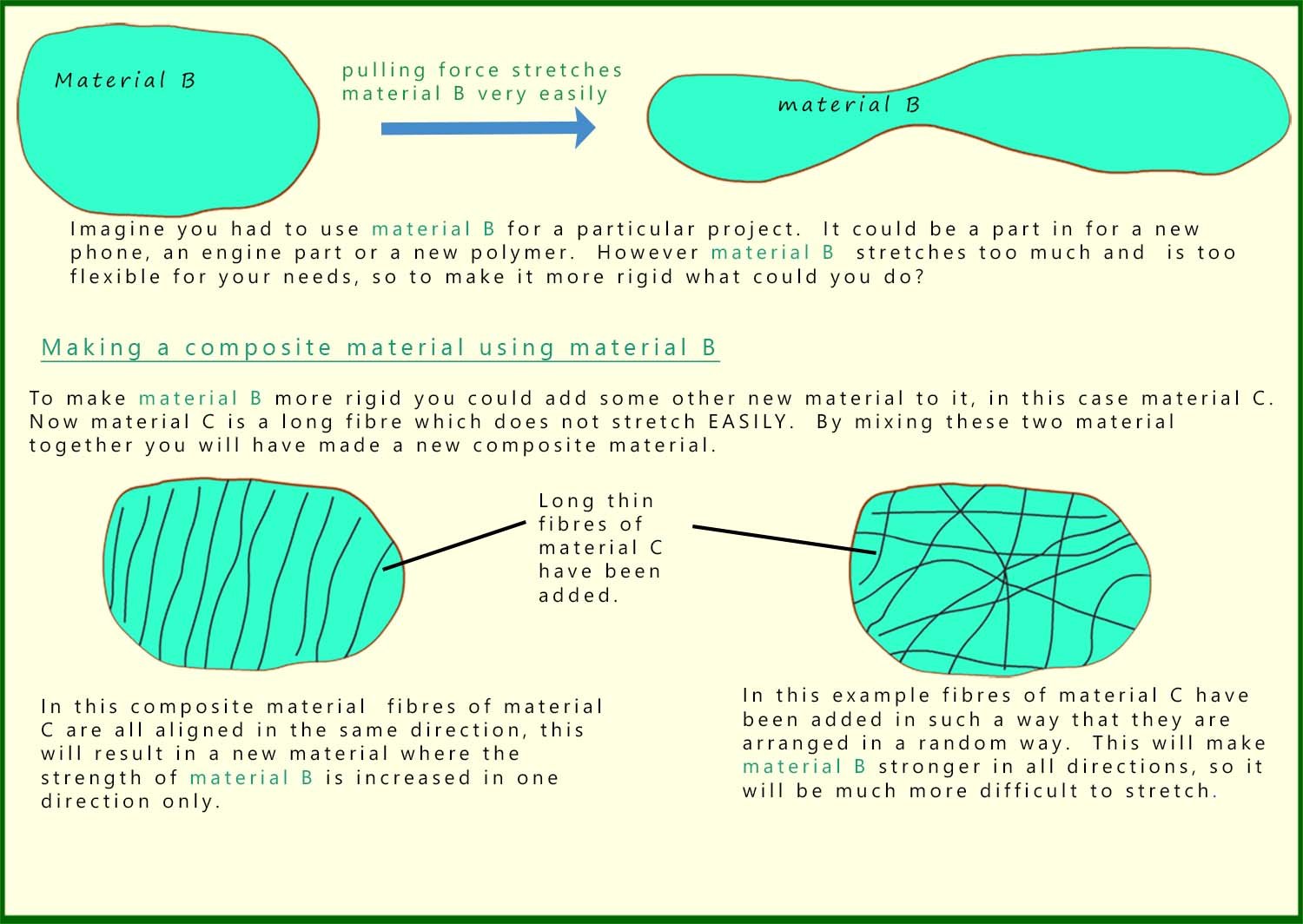
There are two keywords you need to be aware of when describing composite materials; these keywords are: the reinforcement and the matrix (or binder). In a composite material the matrix is the background material; in the example above the matrix is material B. The reinforcement material is usually a fibre or particle which is added to the background material; in the example above, the reinforcement is material C.
The reinforcement is there to absorb the forces and shocks placed on the material in the matrix and the job of the matrix is to hold the reinforcement in place and to protect it from heat, friction or the weather. The matrix material is usually composed of a polymer, a metal or a ceramic material. The image below gives more details on the use of reinforcement materials and the matrix in a composite material.

 Concrete is used mainly in the construction industry; it is used to build up tall buildings such as car parks and
skyscrapers. It is also used for roads and in the foundations for buildings. As a building material it is very strong
in compression, hard wearing and durable but it is brittle especially under tension and stretching, that is it has a low tensile strength (it will crack if it is
forced to stretch). This will obviously limit its uses.
Concrete is used mainly in the construction industry; it is used to build up tall buildings such as car parks and
skyscrapers. It is also used for roads and in the foundations for buildings. As a building material it is very strong
in compression, hard wearing and durable but it is brittle especially under tension and stretching, that is it has a low tensile strength (it will crack if it is
forced to stretch). This will obviously limit its uses.
Metals, such as steel, are also strong in compression but are very strong in
tension; they can support heavy loads when stretched without breaking. The solution to concrete's problem is to embed
reinforcing rods
(often called rebar) made of metal into the wet concrete. When the concrete sets hard you will have a
composite
material which is both strong in compression and strong in tension. The reinforcement material here is the steel rods (rebar), which are embedded in the concrete matrix or binder.
Perhaps one of the most common composite materials is fibreglass or glass reinforced plastic (GRP) as it is sometimes called. Here glass fibres, which are normally woven into a thin flexible sheet, are embedded in a liquid polymer material, often polyester or epoxy, which hardens when it sets. In this composite material the glass fibre woven sheet is the reinforcement. It is strong and stiff but brittle, whereas the liquid polymer, which hardens after a few hours, is the matrix or binder. Thus the resulting fibreglass is stiff, strong and flexible. The image opposite shows one of the many uses of fibreglass, the most common uses include:
 Laminates are also a type of composite material; they are made by joining together two or
more layers of material. Plywood is an example of a laminate material; it is made by bonding many layers of wood together using an adhesive. Alternate
layers of wood are rotated by 90o and then glued to each other; this increases the strength of the plywood and increases its resistance to bending.
Laminates are also a type of composite material; they are made by joining together two or
more layers of material. Plywood is an example of a laminate material; it is made by bonding many layers of wood together using an adhesive. Alternate
layers of wood are rotated by 90o and then glued to each other; this increases the strength of the plywood and increases its resistance to bending.
Other examples of
common laminate composite materials are car windscreens. Here 2 layers of glass have a thin polymer layer sandwiched between them. This
laminated glass has the advantage over "normal" glass in that it will not shatter into large sharp pieces and so will
reduce the risk of serious cuts to anyone unfortunate enough to be involved in a car accident. It will also stop most
objects from passing through it, so will offer some protection to passengers if the windscreen is hit by a small
object.
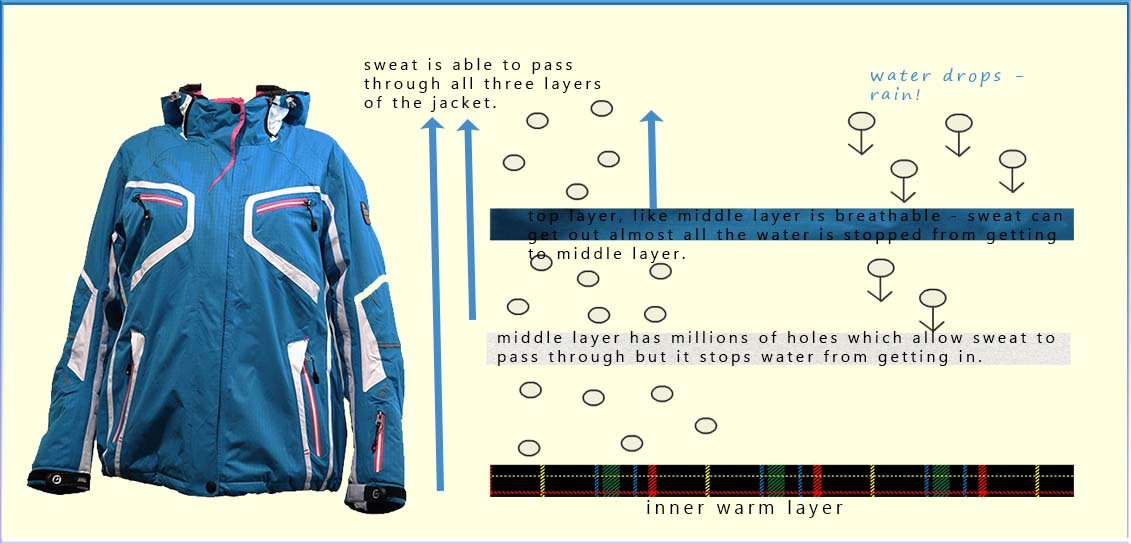
Many outdoor jackets and sportswear are also made of laminate materials. The ski jacket shown in the image below has three different layers of materials. The outside layer is waterproof but breathable and stops most of the rain getting through to the inside of the jacket but allows sweat to pass out. The middle layer is made of a polymer which is also breathable, but this layer stops all water but allows sweat to pass through, this helps keep the wearer comfortable and warm. The inner layer is soft and warm to the skin. In many fabrics the layers may be bonded to each other. Shoes, in particular trainers, are also made of laminated materials. Different laminates and materials can be used for different parts of the shoe or boot.

This page mentions only a few composite materials, however composite materials are widely used because they offer:
Complete the activity below by correctly identifying the matrix and the reinforcement in each composite material.
Click the correct button below each image to show which part is the matrix and which is the reinforcement.
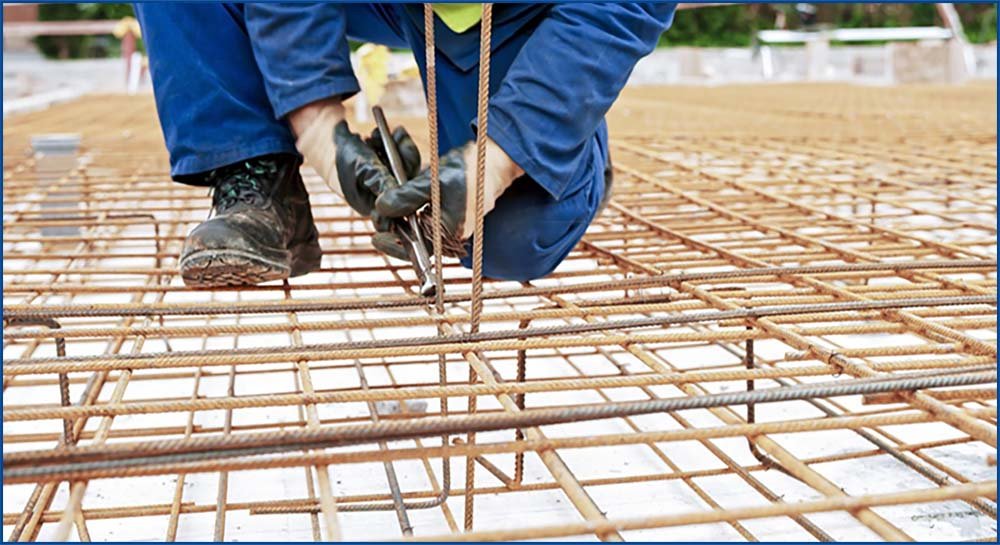

Steel rods in concrete
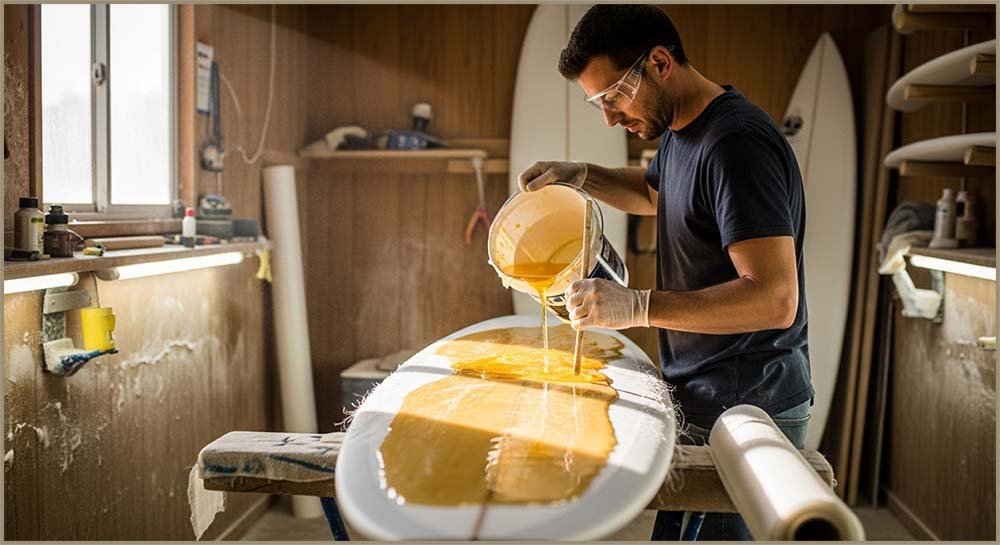

Polymer resin in fibreglass
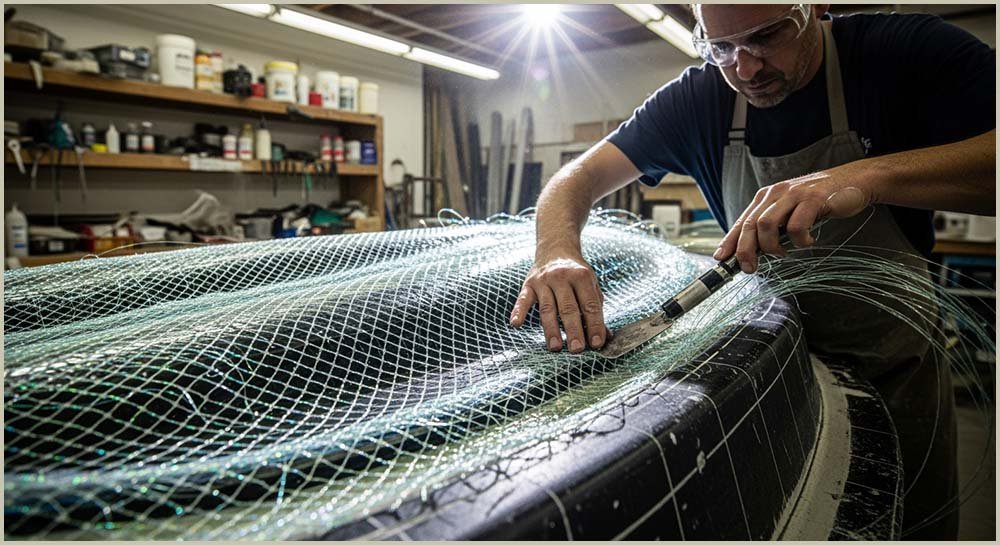

Glass fibres in fibreglass
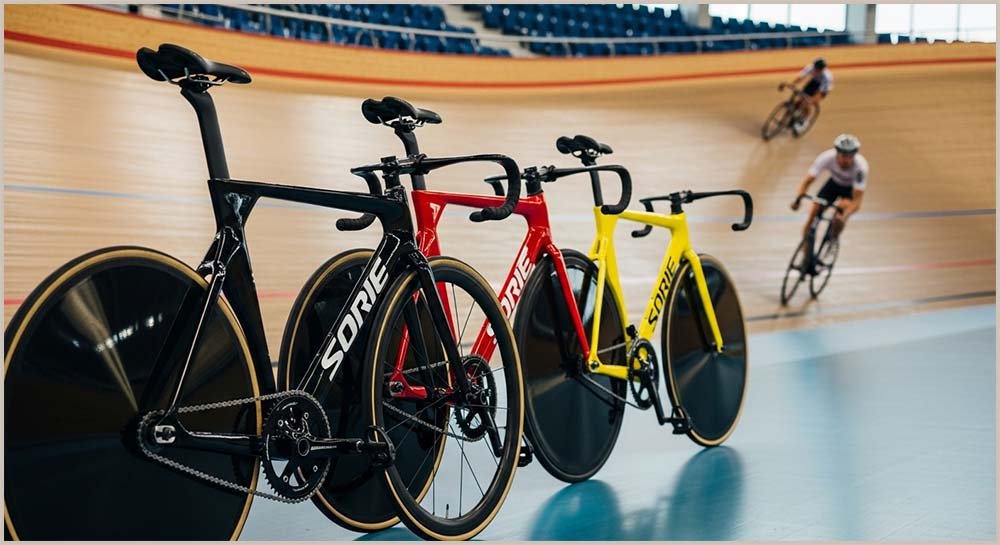

Carbon fibres in a polymer resin (CFRP)
Look at each picture and choose which composite material it shows.

Which composite is this?

Which composite is this?
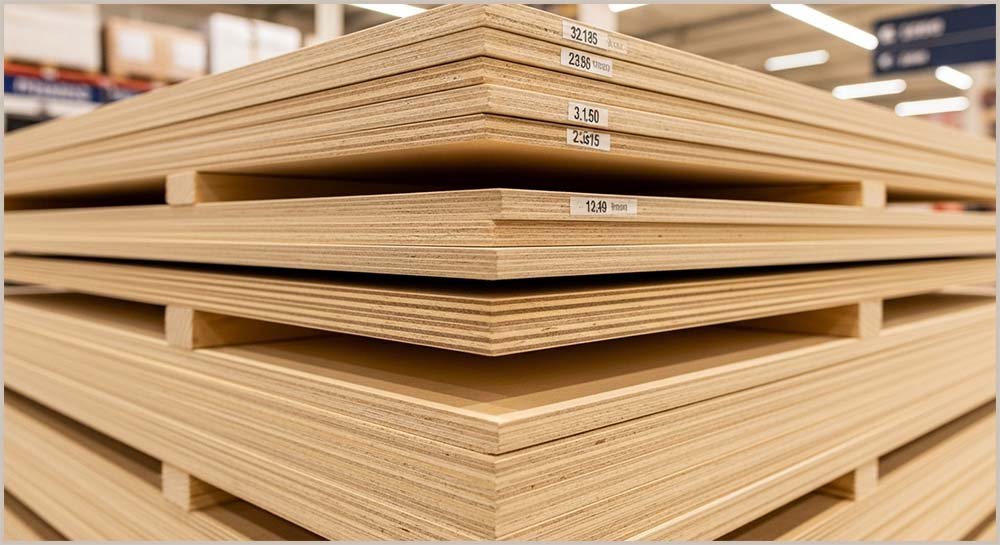

Which composite is this?
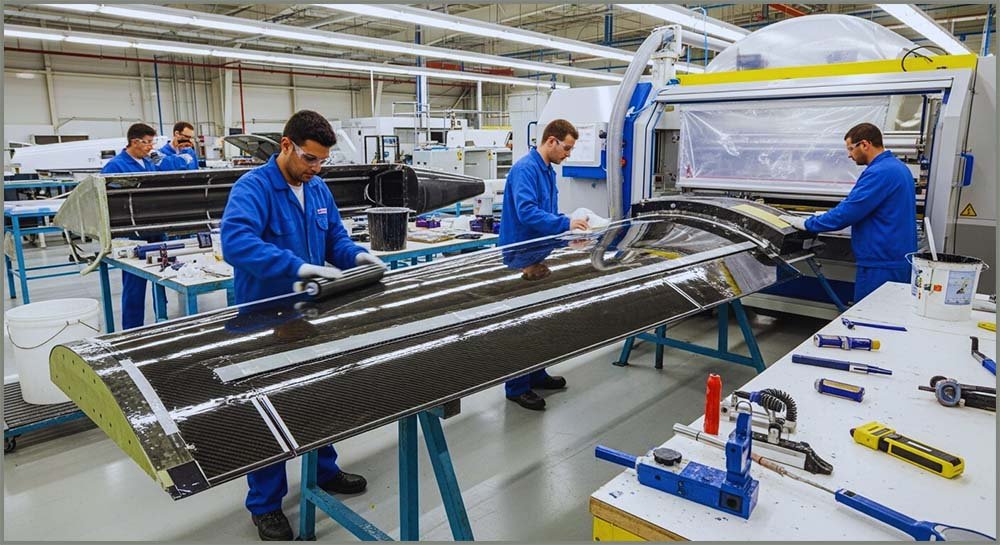

Which composite is this?