

Chemistry only
 The word alcohol is most commonly associated with alcoholic drinks;
unfortunately most alcohols are toxic and are definitely
not suitable for use in drinks. The one alcohol which is safe to consume in small amounts is ethanol; since it is a highly effective intoxicant; that is it causes the desired effects of relaxation and euphoria although it still causes many people to do very silly things when
taken in excess! Ethanol has been made for thousands of years as an alcoholic drink in
a process called fermentation.
As an example consider how beer is made.
The word alcohol is most commonly associated with alcoholic drinks;
unfortunately most alcohols are toxic and are definitely
not suitable for use in drinks. The one alcohol which is safe to consume in small amounts is ethanol; since it is a highly effective intoxicant; that is it causes the desired effects of relaxation and euphoria although it still causes many people to do very silly things when
taken in excess! Ethanol has been made for thousands of years as an alcoholic drink in
a process called fermentation.
As an example consider how beer is made.
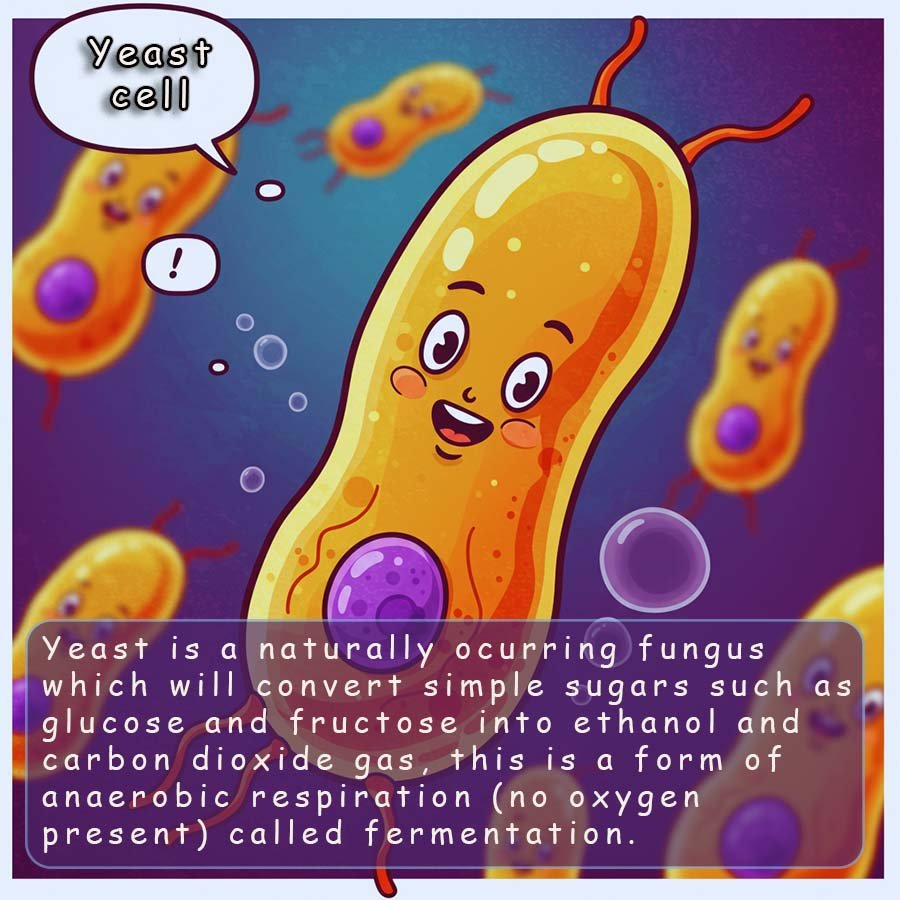
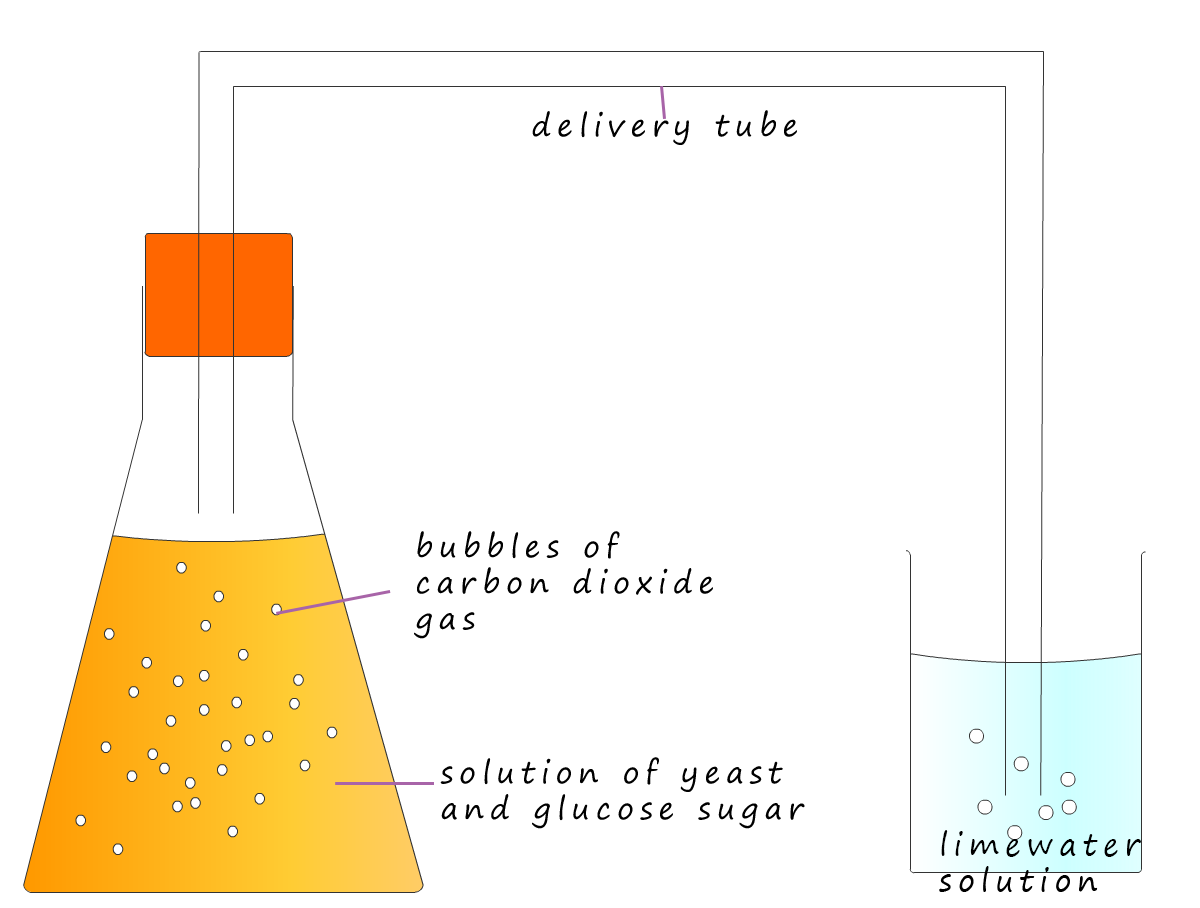
To make beer; barley or sometimes oat grains are allowed to start germinating by being placed in water. After a few days naturally occurring enzymes break down the starch present in these grains into simpler sugar molecules. Yeast is a natural fungus which will produce an enzyme called zymase which will convert the simple sugars in the solution into carbon dioxide gas and the alcohol ethanol. This is fermentation.
The fermentation process is slow and can take days or even weeks. Fermentation is a natural process; it is a form of anaerobic respiration called fermentation. An equation for fermentation is:
Alcohols such as ethanol are found in many hand sanitizers, where they work as a sterilising agent by attacking and breaking down essential parts of a bacterial cell. The ethanol for example acts as a powerful solvent that dissolves the outer membrane or skin of many bacteria cells.
The alcohol also enters the bacteria cell and causes many important proteins inside the bacteria cell to denature; that is they change shape and clump together. This is similar to cooking an egg: the solution inside the cell becomes a solid and stops working. With its outer layer damaged and internal systems broken, the bacterium quickly dies.
Interestingly, alcohol is more effective when mixed with a little water (typically 60–90% alcohol). The water slows down evaporation of the alcohol and helps with the denaturation process of the proteins present inside the bacteria cell, giving the alcohol more time to penetrate and destroy the microbe.
Ethanol is also effective at neutralising many types of viruses, especially enveloped viruses. Recall that viruses are not living organisms like bacteria; they require a host to replicate. These enveloped viruses have an outer fatty membrane or "envelope." Alcohol is very effective at neutralising these viruses because it easily dissolves this fatty membrane layer, just like it breaks down the cell membranes of bacteria. Without its envelope, the virus cannot attach to and infect host cells. Examples of enveloped viruses that alcohol works well against include corona viruses (like the one that causes COVID-19), influenza (flu) viruses, HIV, and herpes viruses.
Use the flashcards below to review your understanding of the main ideas on fermentation covered above:




Alcohol (ethanol) used in alcoholic drinks such as beer, wine and spirits is made by fermentation. However alcohol can also be made a method called direct hydration. Using this method produces alcohol very quickly when compared to fermentation and being the only substance made there is no waste and no costs are needed in separating out unwanted substance. It is also a continuous process whereas traditional fermentation is a batch process. This makes direct hydration much more cost effective and more efficient; however it is a non-renewable process since the unsaturated ethene molecules needed for it comes from crude oil.
The alcohol required for or used in many industrial purposes; where it may be used for example as a solvent and its use sanitizers will be made by the direct hydration method rather than fermentation. Direct hydration simply involves adding steam across the C=C in an alkene molecule, usually ethene. The reaction is shown below. A catalyst (phosphoric acid) and a high temperature (3000C) and high pressure (65 atmospheres) are both needed to get this reaction to occur smoothly.
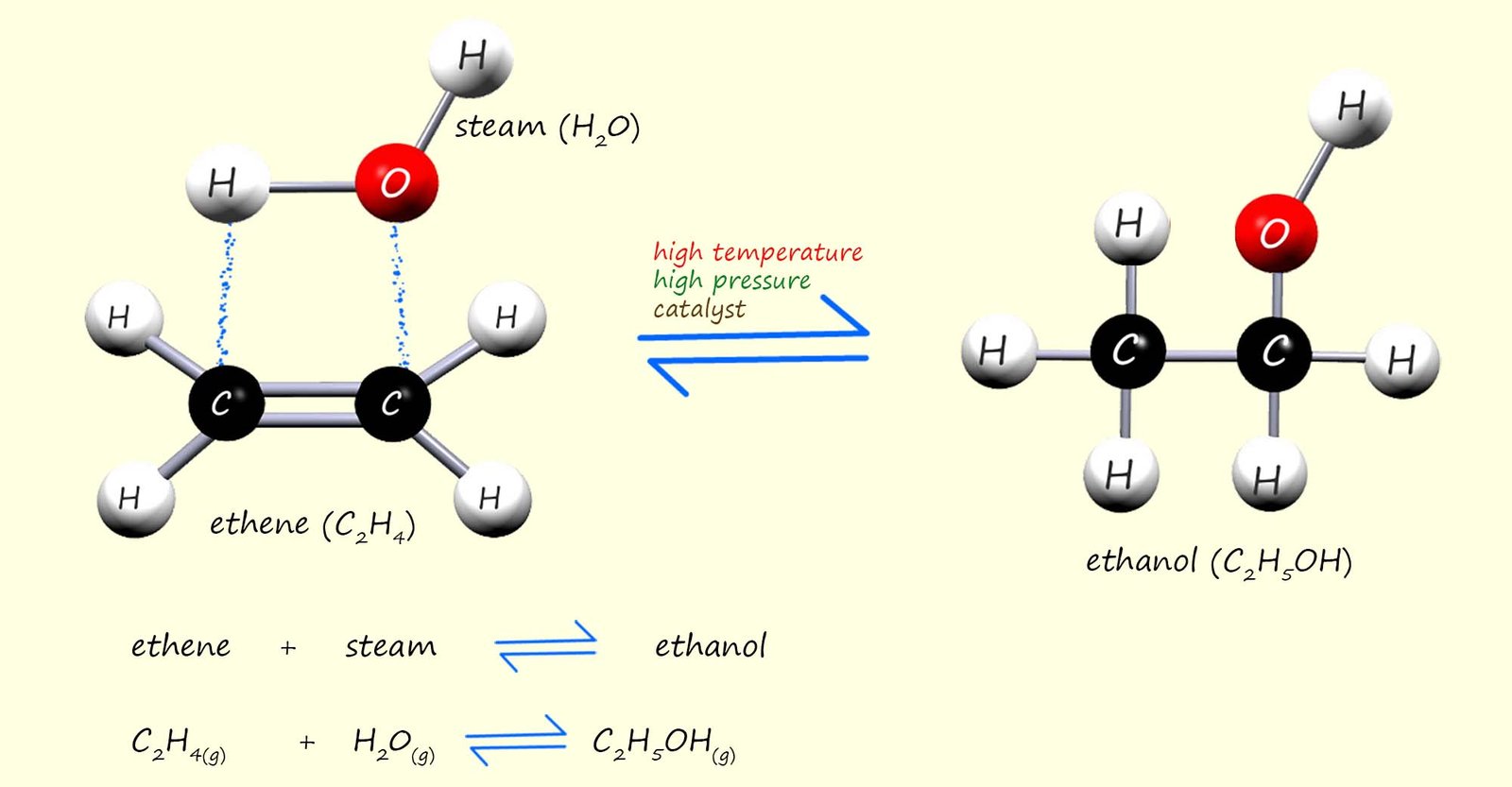
From the equation in the image above you can see that this hydration reaction is a reversible reaction. This means that the products of the reaction will be a mixture of ethanol, steam and unreacted ethene, in fact very little of the ethene and steam react when they first enter the reaction chamber. This mixture of substances formed from the hydration reaction then leaves the reaction vessel and enters a condenser, this is outlined below:
In the condenser the steam and ethanol
 condense and turn back into liquids while the unreacted ethene is recycled back through the reactor to react with more steam, this way the yield of the reaction can be greatly increased. The ethanol and water formed during the reaction mix freely to form a solution which leaves the condenser. The ethanol produced by hydration can be separated from this solution formed by fractional distillation.
condense and turn back into liquids while the unreacted ethene is recycled back through the reactor to react with more steam, this way the yield of the reaction can be greatly increased. The ethanol and water formed during the reaction mix freely to form a solution which leaves the condenser. The ethanol produced by hydration can be separated from this solution formed by fractional distillation.