


Ionic compounds all have a giant ionic lattice structure with all the ions held in place by strong ionic bonds which prevent the ions from moving
freely within the lattice structure. Ionic bonds are strong bonds, however most ionic compounds will dissolve in water;
especially those containing a metal from group I and the bottom end of group II in the periodic table. When an
ionic compound dissolves in water the water
molecules will pull apart the giant lattice structure and we will end up with ions that are separated from each other and able to
move freely within the solution formed, this is outined in the image below:
If an ionic compound is dissolved in water then the solution formed will conduct electricity. The reason for this is that the water molecules are able to form intermolecular bonds to the positive and negataively charged ions present in the giant ionic lattice and pull them free of the lattice structure, it is the presence of these free moving solvated ions that allows the solution to conduct electricity. This is why for example you will get a larger electric shock if you touch a live electrical wire
with wet hands than you would if your hands were dry. Since you sweat salt water (a solution of sodium chloride) this solution will conduct the electricity
and result in a severe electrical shock.

The image below shows the apparatus needed to demonstrate the fact that solutions of ionic compounds
will conduct electricity. In the image you can see that two graphite electrodes are dipped into a solution of an ionic compound, now the positively charged metal ions will be attracted to the negatively charged electrode, the cathode while the negatively charged non-metal ions present will be attracted to the positively chargedelectrode; the anode. It is the presence of these free moving ions that allows the solution to conduct elecricity.

Since ionic compounds have a giant lattice structure with lots and lots of strong bonds between the
ions it takes a lot of
energy to
break all these strong bonds and so ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points.
Sodium chloride (Na+Cl-) for example has a melting point of 8010C while aluminium oxide (Al2O3) which has
smaller ions with a much larger charge than those found in sodium chloride; so this means that the ions can pack together very closely and the
attraction between the ions is much larger; so aluminium oxide has a much higher melting point of 20720C.
When these solid ionic compounds melt the resulting liquids or "melts" contain ions that are free to move. This means that the liquid will conduct electricity.


Many ionic compounds are soluble in water; a phrase which is often used when discussing solubility is "like dissolves like". What this
means is that ionic compounds obviously consist of charged ions, now recall that water is a polar solvent it contains
polar covalent bonds and also a dipole
due to the fact that it contains atoms with partial positive and partial negative charges as shown opposite. Due to the large difference between the electronegativity of oxygen (3.4) and hydrogen atoms (2.1) the O-H bond is a polar one with the hydrogen atoms having a partial positive charge (δ+) and the oxygen atom having a partial negative charge (δ-).
However there are other factors affecting solubility beyond polarity, such as lattice energy and hydration enthalpy, but you will meet these terms latter in your A-level course.
Ion-dipole forces are a type of attraction found between polar solvents such as water molecules and the ions present in an ionic solute. The partial negative charge present on an oxygen atom in a water molecule will be attracted to any positively charged metal ions present in an ionic solute, while the partially positively charged hydrogen atoms in the water molecules will be attracted to any negatively charged an mon-metal anions present in the solute.
In the case of sodium chloride; which contains positively charged sodium ions (Na+) that will attract the partial negative charge on the oxygen atoms in the water molecules; while the negatively charged chloride ions (Cl-) will attract the partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms in the water molecules. This is outlined in the image below:
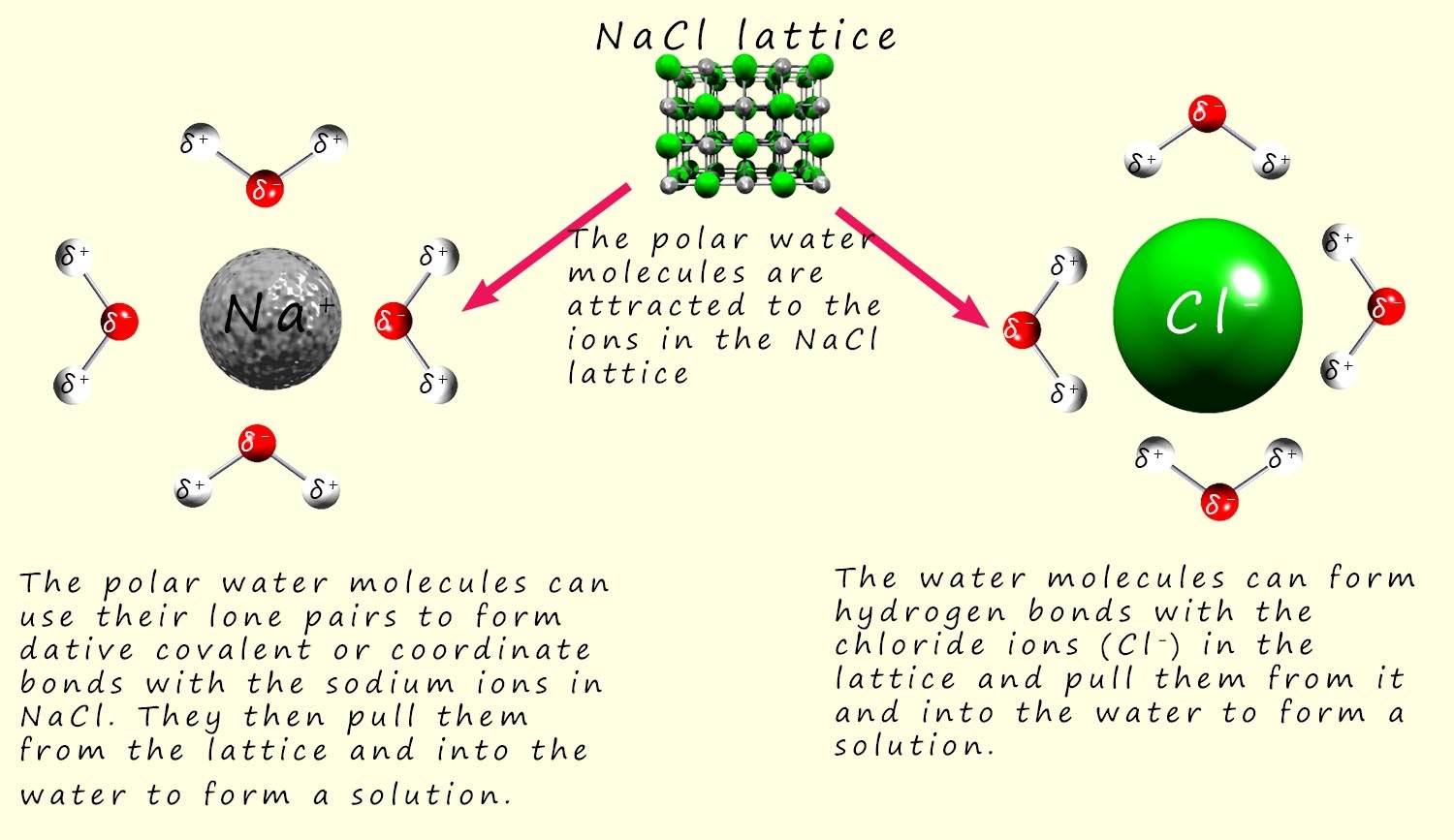
The polar water molecules will be attracted to the positively charged sodium ions (Na+) and the negatively charged chloride ions (Cl-) ions as shown in the image above, a tug of war will now begin where the water molecules will attempt to pull the ions from the lattice and overcome the attractive forces between the oppositely charged ions in the giant ionic lattice. Once the water molecules pull the ions out from the lattice structure they will surround them and form a solvation sphere around each of the ions in solution, this is shown in the image below:
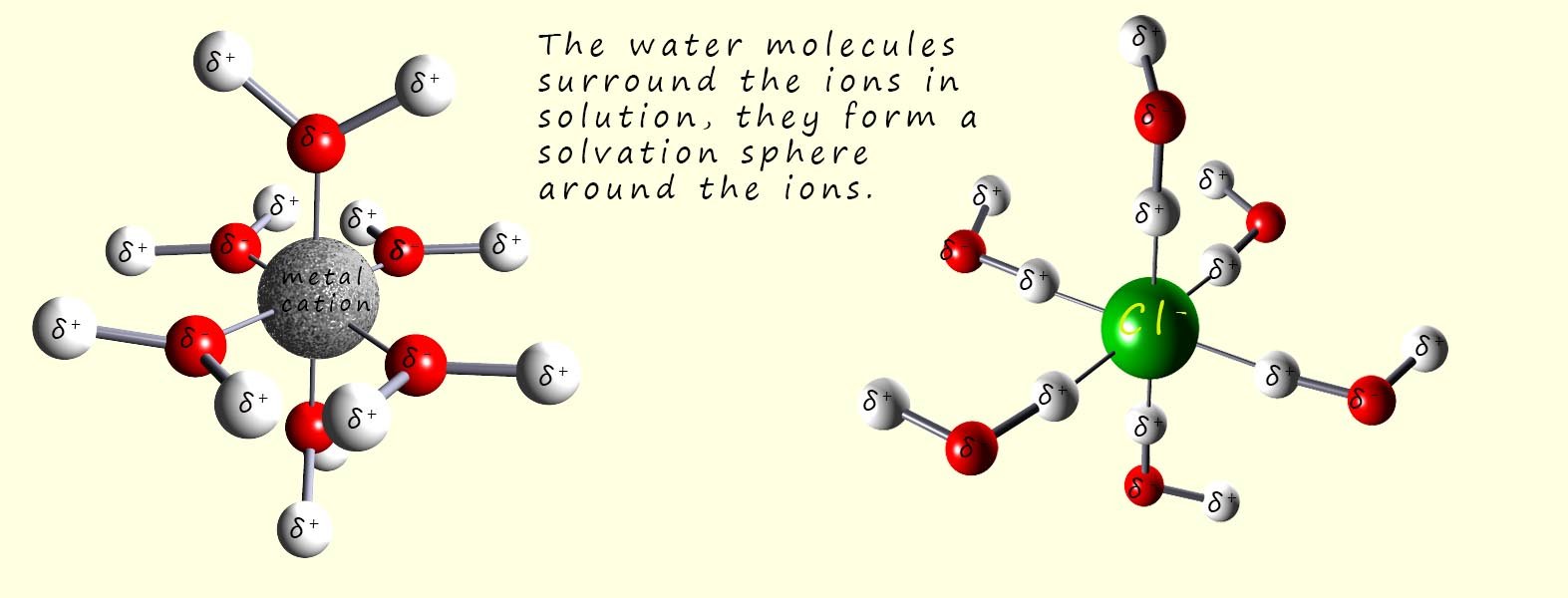
The water molecules form what is called a solvation sphere around the dissolved metal cation and the non-metal anions. The solvation spheres shown in the image above involve six water molecules surrounding the metal cation and the non-metal anion, but in reality you can have a second and third or more solvation spheres surrounding the dissolved ions.
If an ionic lattice is subjected to any pushing or pulling forces which causes the layers of
ions to move this will lead to
widespread cracking within the lattice structure as ions of similar charge are brought in contact with each other. The
ions will
immediately repel each other and the lattice structure will break apart at this point. This means that
ionic lattices are brittle
and can easily break.

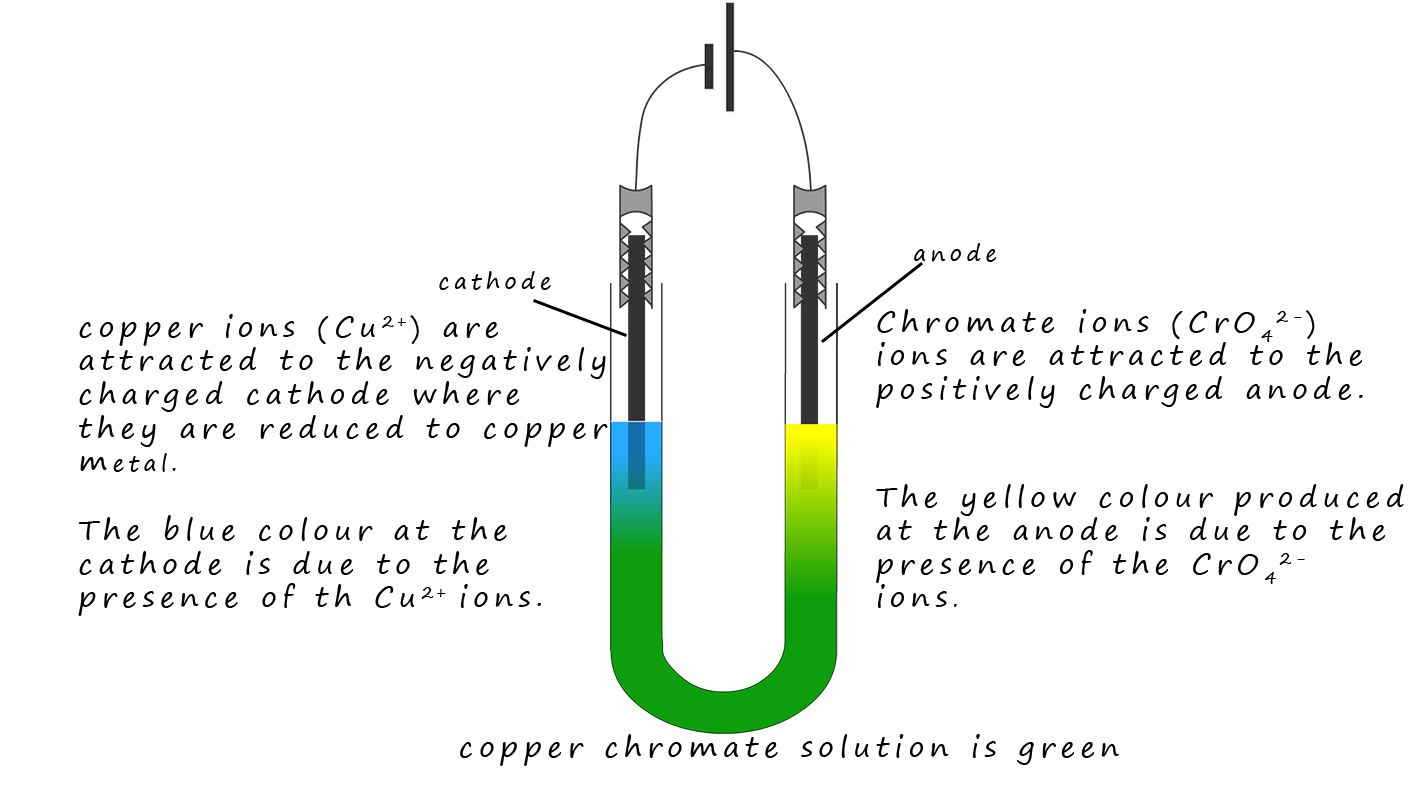 Copper chromate is an ionic compound containing blue copper ions (Cu2+) ions and yellow chromate ions
(CrO42-). These two ions
mix and the resulting solution is green. However when the solution is
electrolysed the positively charged
(Cu2+) ions are attracted to the negatively charged cathode and the
yellow CrO42- ions are attracted to the positively charged anode. This simple
demonstration is a good piece of evidence for the presence of ions in a solution.
Copper chromate is an ionic compound containing blue copper ions (Cu2+) ions and yellow chromate ions
(CrO42-). These two ions
mix and the resulting solution is green. However when the solution is
electrolysed the positively charged
(Cu2+) ions are attracted to the negatively charged cathode and the
yellow CrO42- ions are attracted to the positively charged anode. This simple
demonstration is a good piece of evidence for the presence of ions in a solution.